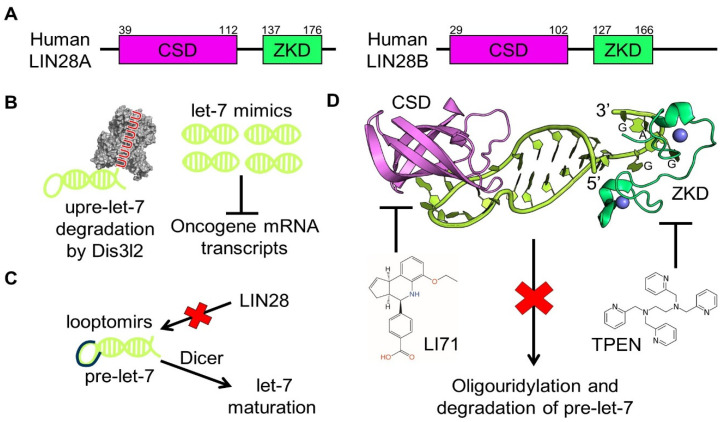
Figure 4.
Pharmacological inhibition of LIN28-driven oncogenesis. (A) Domain architecture of human LIN28A and LIN28B, which share an N-terminal CSD (magenta) and a C-terminal ZKD (green) The residue numbers are denoted atop. (B) Let-7 mimics enhance tumor suppression by replenishing let-7, the level of which is decreased by LIN28-mediated oligouridylation and degradation by nuclease DIS3L2 (grey) (PDB ID: 4PMW). (C) Looptomirs hinder (red cross) LIN28 binding to pre-let-7 without blocking downstream pre-let-7 processing by Dicer, thereby promoting let-7 maturation. (D) Small molecules LI71 and TPEN inhibit (red cross) LIN28 by targeting its CSD and ZKD, respectively. Crystal structure of human LIN28A in complex with pre-let-7f-1 (yellow) (PDB ID: 5UDZ). Zn2+ ions (blue) are visible near the ZKD. The GGAG motif in pre-let-7f-1 is indicated near its 3′ end.