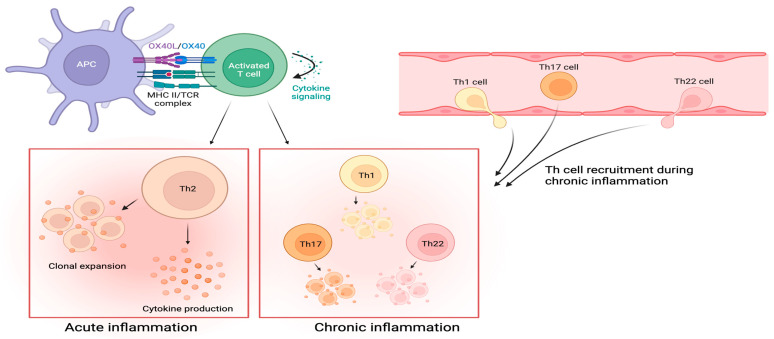
Figure 4.
Two phases of inflammation characterize AD. During the acute phase, OX40-OX40L ligation on activated T cells facilitates TH2-predominant signaling and differentiation, which produces type 2 inflammatory cytokines. The shift to the chronic phase is characterized by the recruitment of TH1, TH17, and TH22 cells expressing OX40. OX40-OX40L ligation on these activated T helper cell populations leads to effector cell proliferation and cytokine production that maintain the inflammatory response.