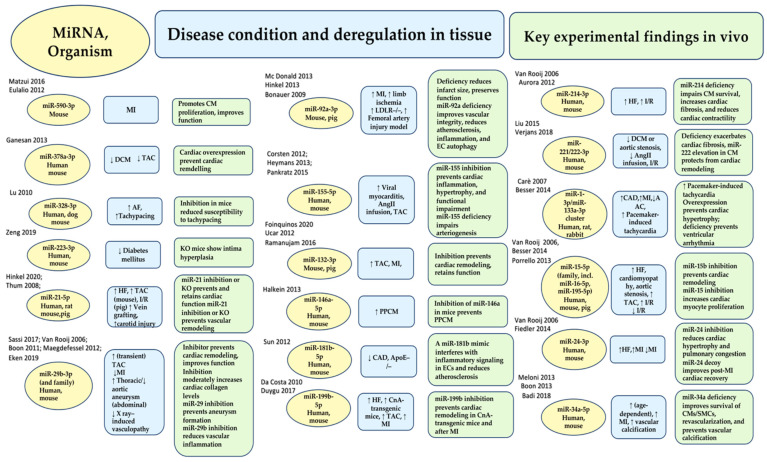
Figure 1.
MiRNAs play a crucial role in the cardiovascular system. They are implicated in disease and disease phenotypes, and their effects can be engineered in vivo. The figure shows miRNA species and organisms under investigation (yellow), the disease state and regulation (blue), and key experimental evidence in vivo (green). Abbreviations: AF, atrial fibrillation; AngII, angiotensin II; CAD, coronary artery disease; CnA, human calcineurin subunit A; DCM, dilated cardiomyopathy; HF, heart failure; I/R, cardiac ischemia–reperfusion; CM, cardiac myocyte; EC, endothelial cell; KO, knockout; SMC, smooth muscle cell; MI; myocardial infarction; PPCM, peripartum cardiomyopathy; AAC/TAC, ascending/transverse aortic constriction. From Nappi et al. ref [12]; Refs. [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] in the figure. Up arrow = increase, Down arrow = decrease.