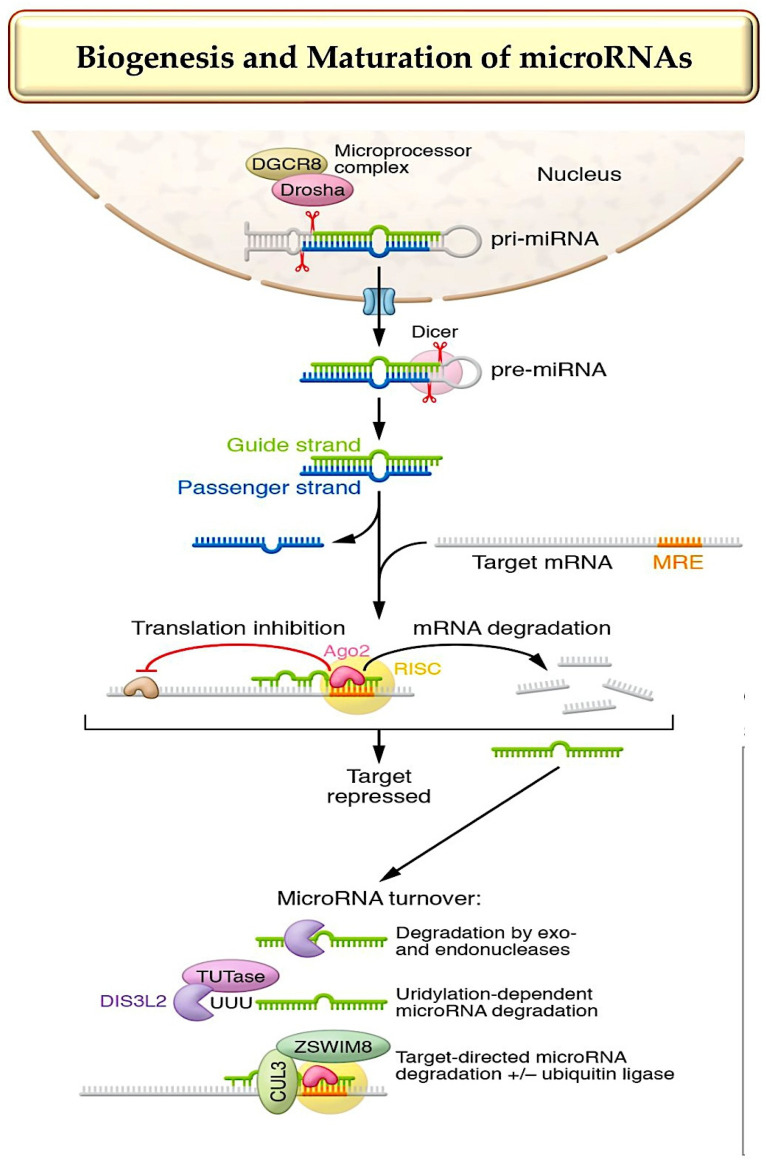
Figure 2.
The diagram shows how miRNAs biogenised and function. Three main steps are involved in the synthesis and release of nuclear pre-miRNAs into the cytoplasm, where the final synthesis of activated RNAs is promoted in parallel with the production of miRNA duplexes, RISC complexes, and RNAi: (A) canonical elaboration, functional activation, mechanism of action and degradation pathways of microRNAs are reported. Canonical miRNA biogenesis starts with larger hairpin RNA molecules (pre-miRNAs). These are produced by RNA Pol II transcription of miRNA genes or clusters or occur as part of introns. In the next step, a microprocessor complex, which includes the endonuclease Drosha, the DGCR8 protein, and other factors, cleaves these molecules. Abbreviations: DGCR8, DiGeorge critical region 8 protein; DIS3L2, DIS3-like 3′–5′ exoribonuclease 2; miRNA, microRNA; miRNA duplex, precursor miRNA; RISC complex, RNA-induced silencing complex; RNAi, RNA activation; TDMD, target-directed microRNA degradation; TUTases, terminal uridyltransferases. Refs. [50,51,52].