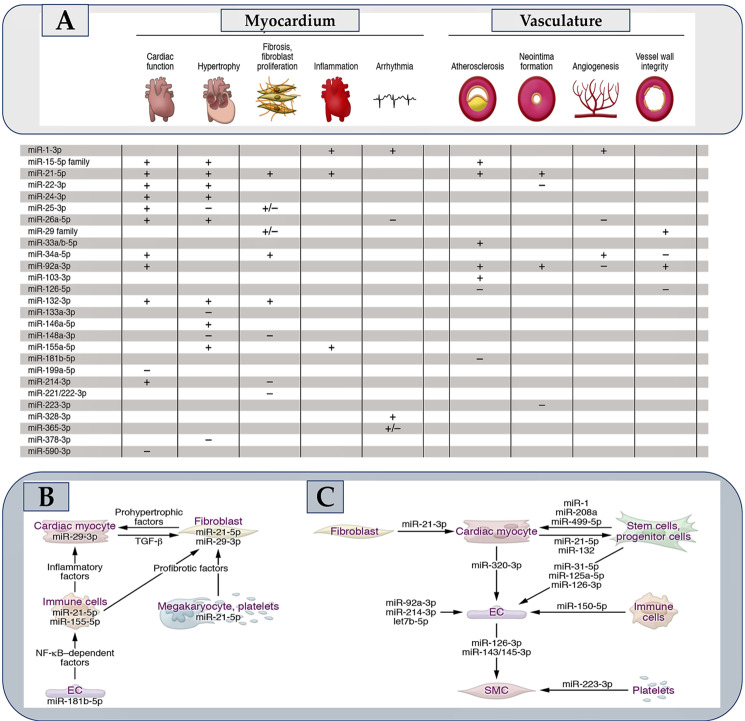
Figure 3.
(A) summarizes the role of miRNAs in heart muscle and blood vessels. The miRNA that promotes a process is marked with a + sign, and the − sign denotes the miRNA that prevents a pathophysiological process. The microRNAs that either promote or inhibit cardiac function when their levels are elevated or inhibited are described in the respective sections. (B) describes microRNAs that regulate the targets responsible for intercellular communication in the cardiovascular system. (C) explains the paracrine roles of specific miRNAs secreted within the cardiovascular system. In contrast, the miR-21 core fragment released by endometrial mesenchymal stem cells has cardioprotective effects by promoting cell survival and angiogenesis. Similarly, miRNAs from the myocardium promote the mobilization of progenitor cells in the bone marrow. Platelets carry miR-223-3p, which regulates the differentiation and proliferation of vascular SMCs. Refer to Ref. [50] for a survey of different cardiovascular microRNAs with suggested paracrine activity. Abbreviations: EC, endothelial cell; miRNA, microRNA; SMC, smooth muscle cell. From Laggerbauer B et al. [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,55,78,79,80,81,82,83,84].