Table 1.
Listing of the reference NMDAR modulators.
| Compounds | Modulator | Selectivity | Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
D-AP5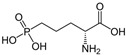
|
Competitive antagonist | GluN2A | Inhibits excitatory response. Impacts behavioral learning; blocks plasticity (LTP). | [95,96,97] |
Riluzole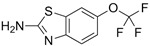
|
Competitive antagonist | GluN1/GluN2B | Indirect block of NMDAR. Protects from motor deficit. | [103,104,105] |
Phencyclidine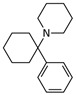
|
Selective uncompetitive antagonist | GluN2B/D(PCP site) | Induces psychotic and dissociative schizophrenia-like symptoms. Impairs NMDAR neurotransmission in vivo. | [98] |
Ketamine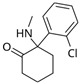
|
Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN2B/D(PCP site) | Applied in post-synapse: inhibits excitatory pyramidal neuron in extra-synaptic GluN2B. Applied in pre-synapse: inhibits GluN2D in interneuron (induces disinhibition of Glu release in post-synapse). Up-regulates hippocampal AMPARs (GluA1/GluA2). Antidepressant. | [100,106] |
Dizocilpine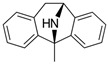
|
Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN2A/B/D(PCP site) | Anticonvulsant, antidepressant. Induces memory impairments. | [102,107] |
Ifenprodil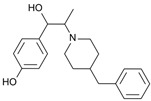
|
Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN1/GluN2B(N-Terminal domain) | Blocks GluN2B (140-fold preference for NR2B over NR2A subunits). Induces inhibition of GluN2R receptor currents. Anti-Parkinsonian effect. | [108,109,110] |
Memantine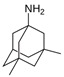
|
Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN1/GluN2B | Blocks GluN2B extra-synaptic and induces glutamatergic excitotoxicity. Used for moderate-to-severe AD. | [111,112] |
Amantadine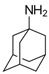
|
Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN1/GluN2B | Blocks GluN1/GluN2B by accelerating channel closure during channel block. Used as anti-Parkinsonian drug. | [113] |
Dextromethorphan
|
Uncompetitive antagonist | GluN2A | Blocks GluN2A subunit. Prevents neuronal damage and modulates pain sensation | [114,115,116,117,118] |
