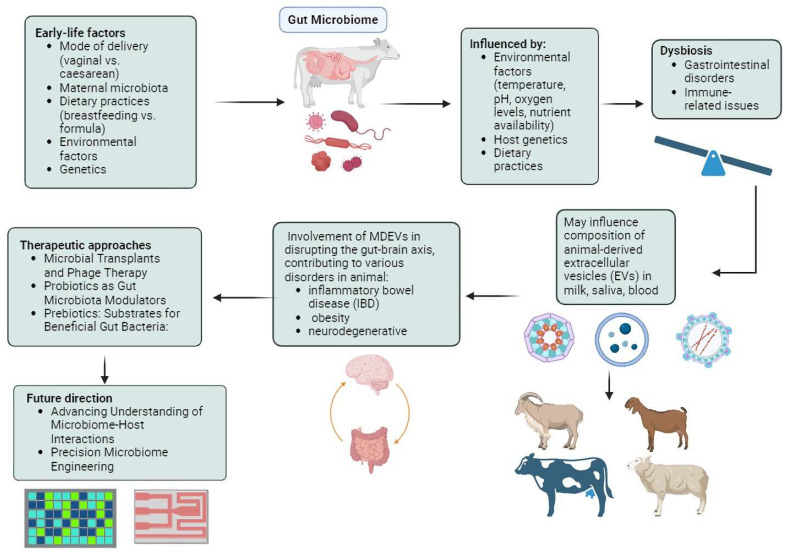
Figure 1.
Environmental factors such as temperature, pH, oxygen levels, and nutrient availability profoundly shape the composition and diversity of the intestinal microbiota in animals, influencing their health and metabolism. Gut microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs), particularly exosomes, play crucial roles in intercellular communication, impacting immune response, neuroinflammation, and metabolic dysfunction. Therapeutic interventions like probiotics, prebiotics, microbial transplants, organic acids, and phage therapy offer promising avenues for modulating the gut microbiota, improving growth performance, health outcomes, and disease resilience in animals.