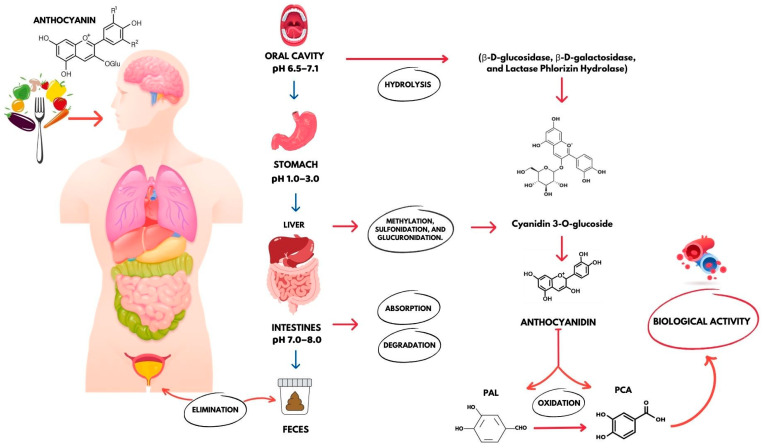
Figure 2.
Absorption process of anthocyanin-derived PCA in the human body: absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination. The absorption of nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract is influenced by the pH of the gastrointestinal tract, which varies significantly between different sectors, ranging from 1.0 to 8.0. Once in the blood, protocatechuic acid (PCA) demonstrates not only antioxidant activity, but also various health-promoting properties, such as anticancer, anti-inflammatory, disease protection, and organ enhancement.