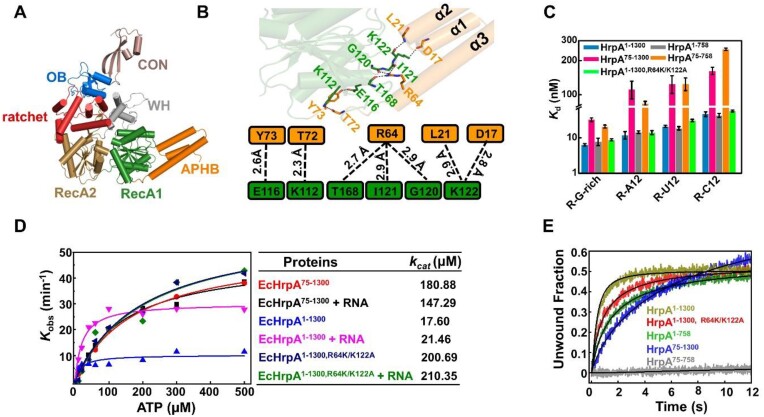
Figure 2.
Structural and Functional Analysis of N-terminal domain APHB (A) Overall Structures of HrpA1-758 apo. All domains are colored and labeled according to Figure 1A. (B) Interactions between APHB and RecA1 domains in the structure of Apo-HrpA1-758 complex structure. Detailed contacts and their schematic representations are shown in the down panel. The dashed line indicates all hydrogen bonds. (C) Dissociation equilibrium constants of HrpA1–1300 and its variants to ssRNA. (D) ATPase assays show that APHB reduces the ATPase activity both in the presence and absence of RNA. (E) Kinetic unwinding curves of HrpA1–1300 and its variants were determined by stopped-flow assay with 4 nM partial dsRNA (with 3′-tail), 100 nM proteins and 1 mM ATP.