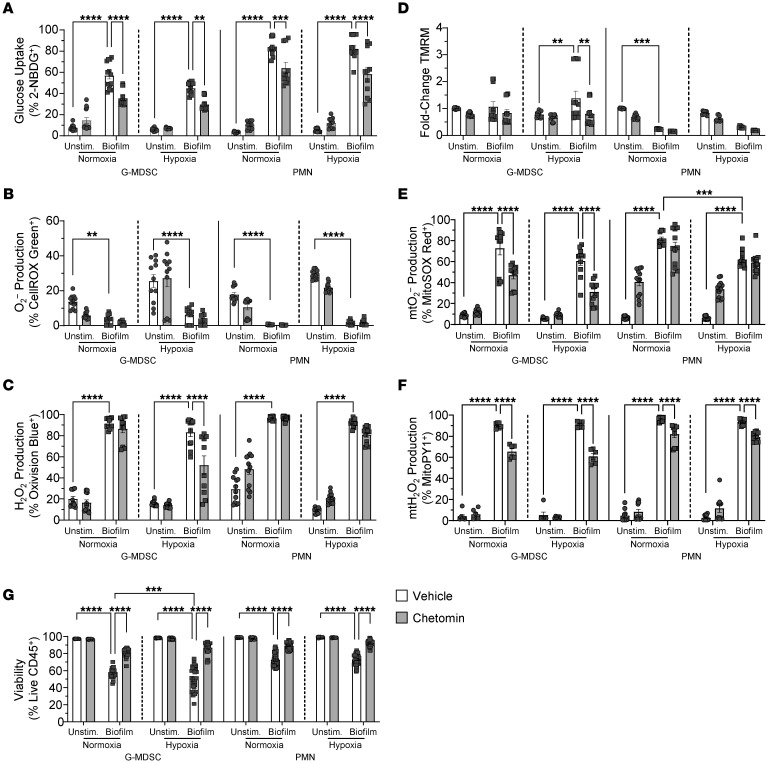
Figure 6. Inhibition of HIF1a signaling attenuates granulocyte ROS production in response to S. aureus biofilm.
Primary G-MDSCs or PMNs were treated with either chetomin or vehicle for 1 hour under normoxia or hypoxia (1% O2) prior to coculture with S. aureus biofilm for 30 minutes under the same oxygen conditions, whereupon cells were stained with (A) 2-NBDG (glucose uptake) (G-MDSC, n = 13/group; PMN, n = 11/group), (B) CellROX Green (O2–) (G-MDSC, n = 11/group; PMN, n = 12/group), (C) OxiVision (H2O2) (G-MDSC, n = 11/group, except for hypoxia/chetomin/biofilm, n = 10; PMN, n = 12/group), (D) TMRM (mitochondrial transmembrane potential; mtMP) (G-MDSC, n = 12/group; PMN, n = 9/group), (E) MitoSOX (mtO2–) (G-MDSC, n = 11/group; PMN, n = 12/group), and (F) MitoPY (mtH2O2) (G-MDSC, n = 6/group; PMN, n = 10/group). (G) Cell viability data are represented as the percentage of live CD45+ cells (G-MDSC, n = 28/group, except for hypoxia/chetomin/biofilm, n = 27; PMN, n = 40/group). Results are represented as means ± SEM of positively stained or fold change (TMRM) in granulocytes cocultured with biofilm versus unstimulated cells under normoxia or hypoxia. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction.