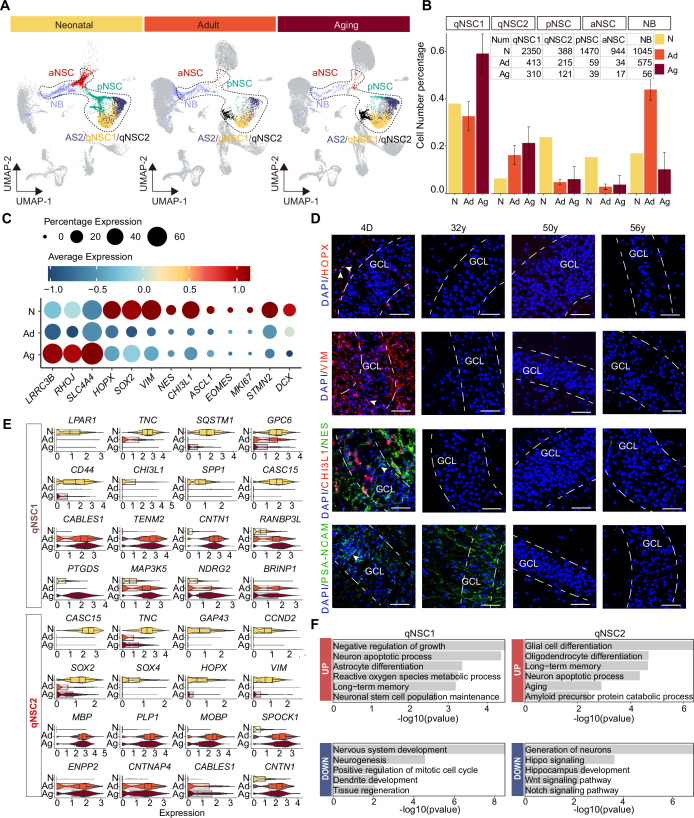
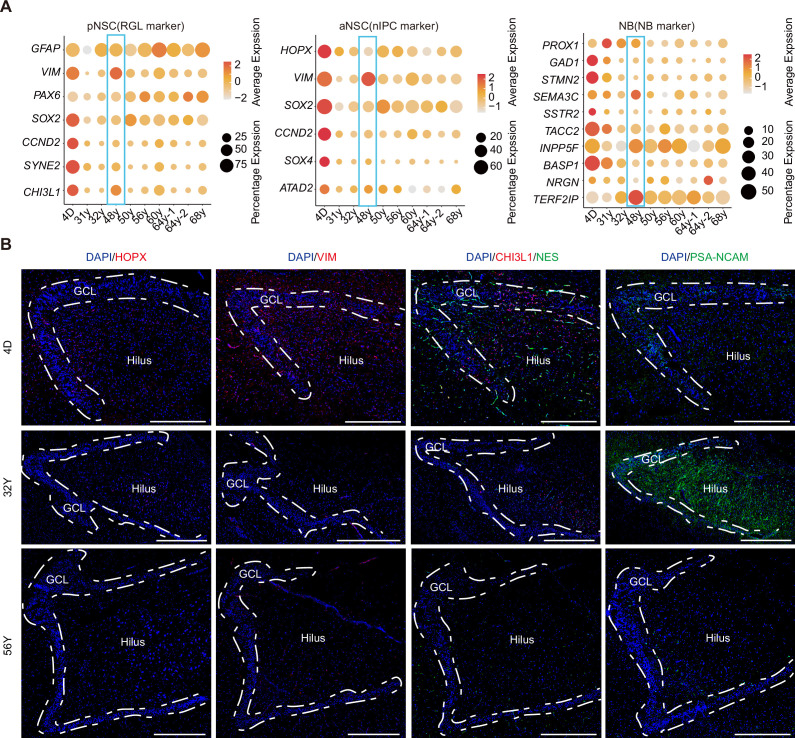
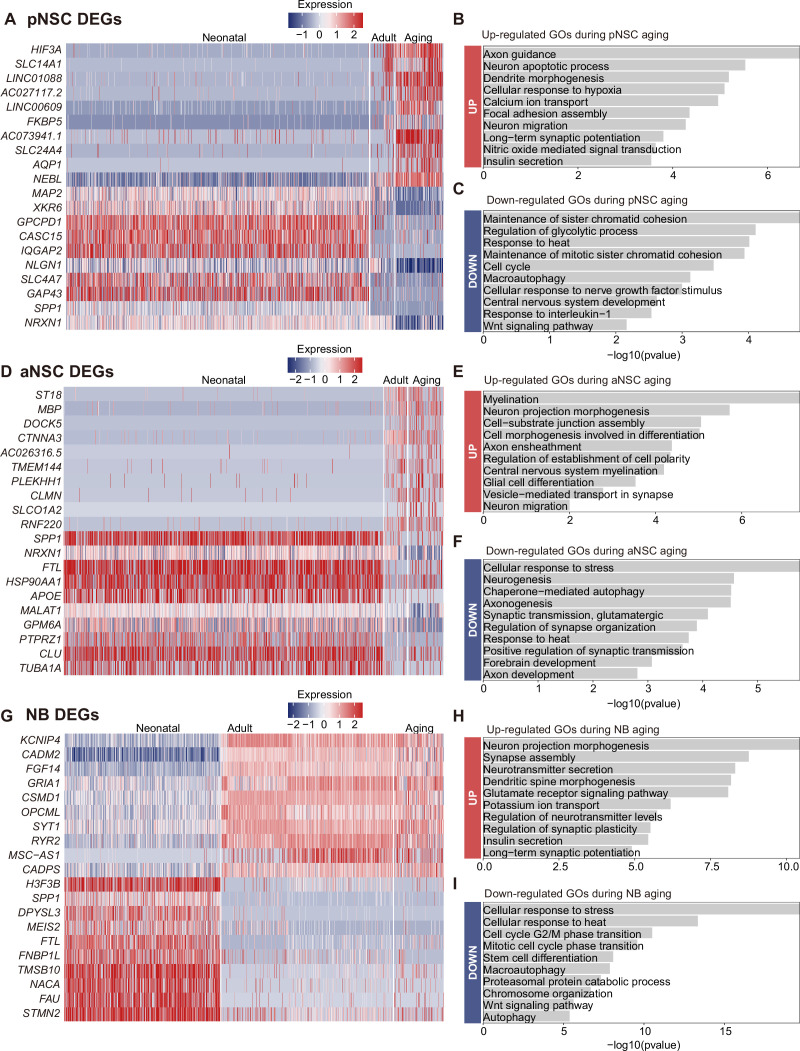
Figure 5. Age-dependent molecular alterations of the hippocampal neural stem cells (NSCs) and neuroblasts (NBs).
(A and B) Feature plots (A) and quantification (B) of the neurogenic populations during aging. Neonatal (abbreviated as N), adult ( abbreviated as Ad), aging ( abbreviated as Ag). The neurogenic populations include qNSC1, qNSC2, pNSC, aNSC, and neuroblast. (C) The dynamic expression of some representative genes, including newly identified qNSCs genes (LRRC3B, RHOJ, and SLC4A4), NSC genes (HOPX, SOX2, VIM, NES, and CHI3L1), neural progenitor or proliferation genes (ASCL1, EOMES, and MKI67), and immature granule cell genes (STMN2 and DCX), in human hippocampus across neonatal (postnatal day4), adult (31y, 32y), and aging (50y, 56y, 60y, 64y-1, 64y-2, 68y). (D) Immunostaining of classical NSC markers (HOPX, VIM, and NES) in human hippocampal dentate gyrus across different ages (postnatal day 4, 32y, 50y, 56y). Scale bars, 60 μm. The arrowheads indicate positive cells with typical morphology. (E) Violin plot showing differentially expressed genes of qNSC1 and qNSC2 in the aging group compared to the neonatal group. (F) Representative gene ontology (GO) terms of significantly (p-value <0.05) up- and down-regulated genes in qNSC1 and qNSC2 during aging.