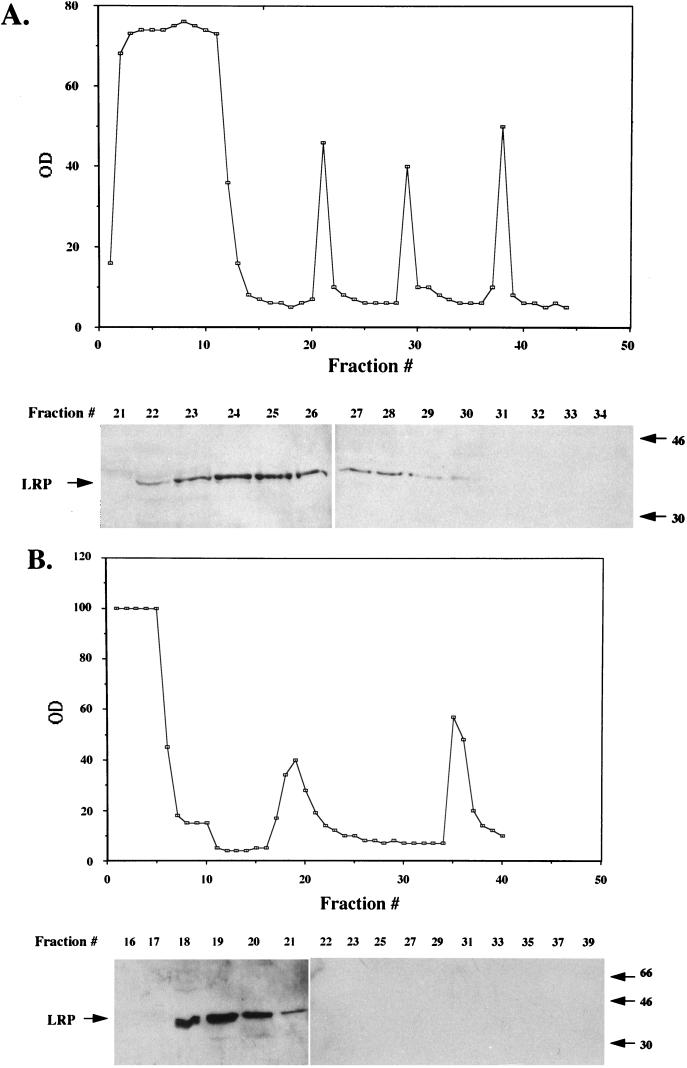
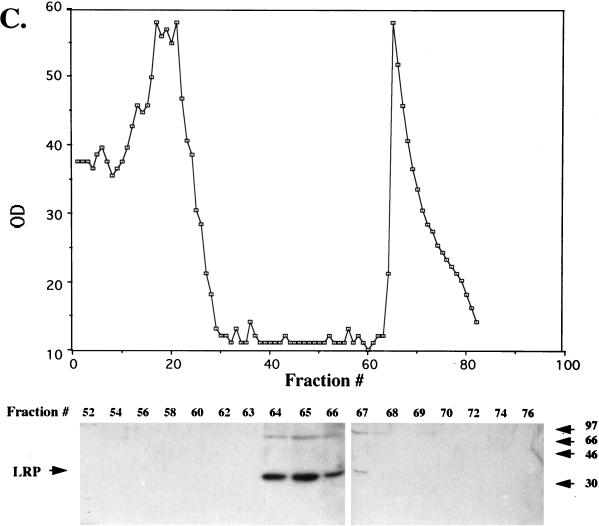
FIG. 8.
Partial purification of LRP from productively infected MDBK cells. Nuclear extract from productively infected MDBK cells (36 hpi, 5 × 109 cells, approximately 645 mg of protein) was applied to a DEAE column, and fractions were collected (A). The graph shows the OD280 of each fraction. LRP was detected with the P2 antibody (fractions containing LRP and the surrounding fractions are shown at the bottom). Other fractions did not contain detectable LRP. (B) Fractions containing LRP from the DEAE column (approximately 200 mg of protein) were pooled and applied to Econo S columns, and protein in each fraction was measured at OD280 (OD values were 20 times less than the values in the graph). LRP-containing fractions were identified by Western blot analysis (bottom). Other fractions do not contain detectable levels of LRP. (C) Fractions containing LRP from the Econo S column were pooled (approximately 4 mg of protein) and applied to the heparin-agarose column. The OD values were 40 times less than the values in the graph. LRP-containing fractions were detected by Western blot analysis using the P2 antibody. Columns were washed, and bound proteins were eluted as described in Materials and Methods. All fractions were analyzed by Western blot analysis, and only those regions of the columns containing LRP are shown. After heparin-agarose chromatography, approximately 600 μg of protein was present in the LRP-containing fractions. These diagrams are representative of at least nine different preparations. In all panels, sizes in the blots are indicated in kilodaltons.