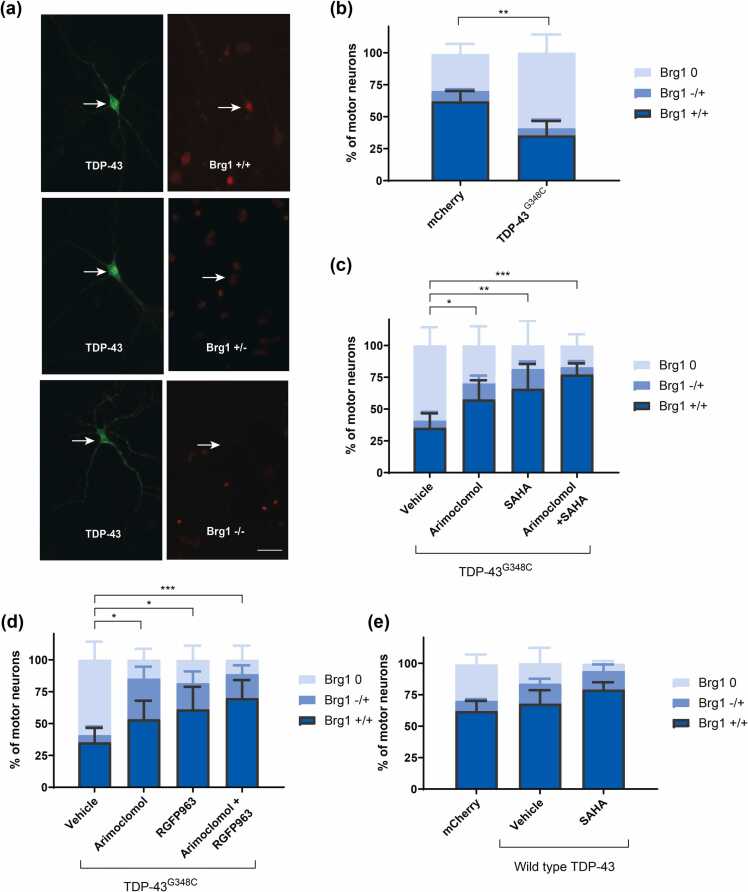
Fig. 8.
HDAC inhibitors and arimoclomol preserve Brg1, the ATPase component of nBAF chromatin remodeling complexes, in TDP-43G348C-expressing motor neurons. Three days after microinjection, cultures were immunolabeled with rabbit anti-Brg1 and mouse anti-flag M2 to visualize TDP-43G348C. (a) Intensity of Brg1 immunolabeling in the nucleus was categorized as: strong (+/+), (+/−), or none (−/−). (b) Compared to controls (mCherry), expression of TDP-43G348C significantly reduced the percentage of motor neurons displaying strong Brg1 labeling. This percentage was maintained similar to controls by (c) SAHA and (d) RGFP963 treatments. Arimoclomol also maintained nuclear Brg1 expression, although slightly less efficiently than HDAC inhibitors. When SAHA or RGFP963 was combined with arimoclomol, a modest enhancement occurred. (e) Brg1 distribution was not significantly affected by overexpression of wild-type TDP-43. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Each data point on the graph represents the mean % of neurons in each of 4–15 cultures (13–39 neurons/culture). Statistical significance was evaluated through one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Scale bar = 20 µm. Abbreviations used: HDAC, histone deacetylase; nBAF, neuronal Brm/Brg-associated factor; SAHA, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid; SD, standard deviation; TDP-43, TAR DNA binding protein 43 kDa.