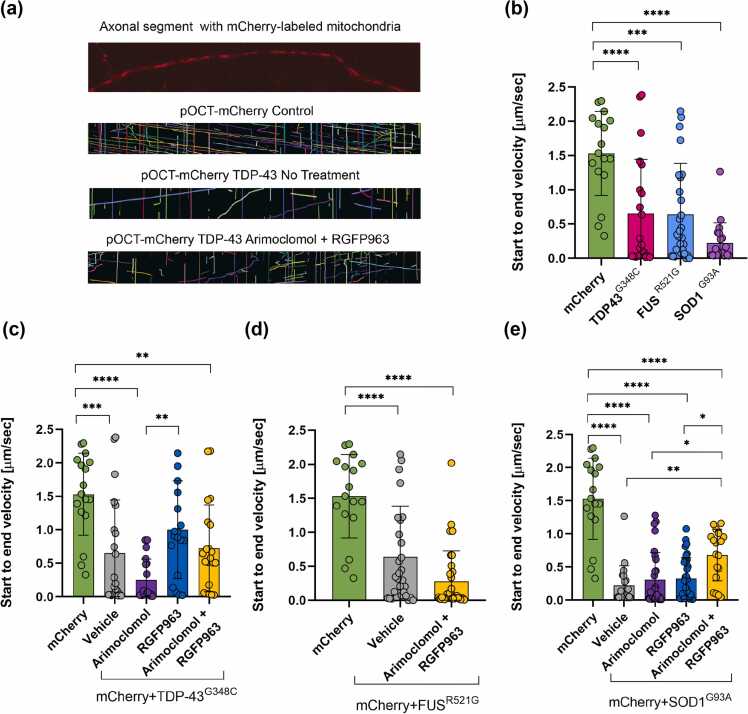
Fig. 9.
Effect of ALS variants and drug treatments on axonal transport of mitochondria. (a) Image of axonal segment of motor neuron expressing pOCT-mCherry localized to mitochondria. Kymographs generated from mitochondrial movements in control or TDP-43G348C-expressing neurons and in cultures treated with vehicle or the combination of arimoclomol and RGFP963. Individual mitochondria were color-coded using KymoResliceWide. Scale bars = 20 µm horizontal and 3.5 min vertical. (b) TDP-43G348C, FUSR521G, or SOD1G93A impaired start-to-end velocity of mitochondrial transport in axonal segments of motor neurons compared to mCherry alone. (c) Neither RGFP963 nor arimoclomol preserved mitochondrial transport in neurons expressing TD-P43G348C or (d) FUSR521G. Only the combination of RGFP963 and arimoclomol reduced the decline in mitochondrial transport by SOD1G93A. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 17–33 axons per group. Statistical significance was evaluated through one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Abbreviations used: ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FUS, fused in sarcoma; SD, standard deviation; SOD1, superoxide dismutase I; TDP-43, TAR DNA binding protein 43 kDa.