Fig. 2.
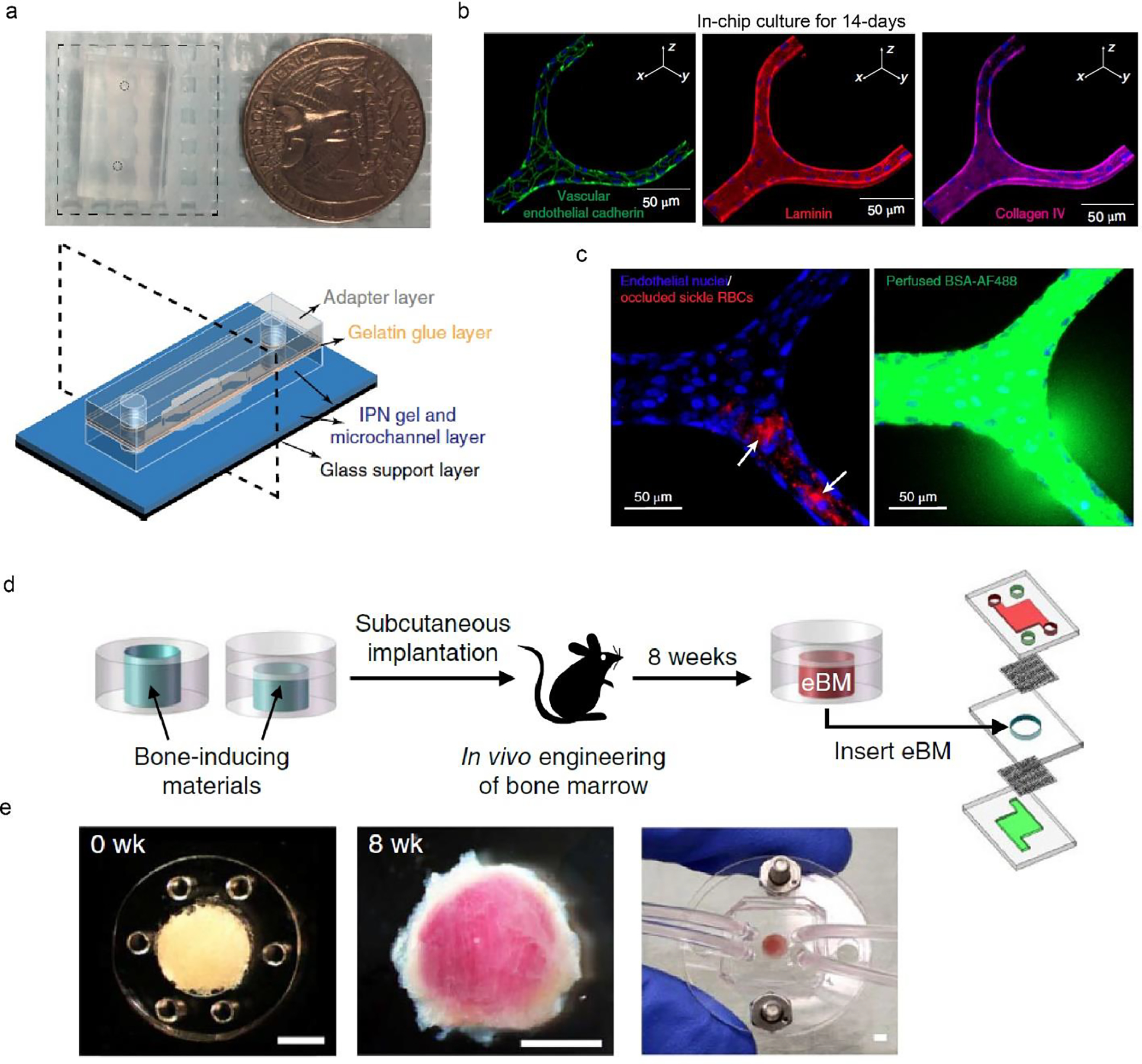
Two tissue chips for recapitulating the blood vessel and the bone marrow. a. Macroscopic view of a blood vessel chip, the size of which is compared with a quarter. Schematic of the tissue chip design, including glass support layer and several hydrogel layers. b. Immunostaining of endothelial cells after 14-day in-chip culture. c. Blockage of sickle RBCs in the engineered vessel leads to local leakage. a-c, Reproduced with permission (Qiu et al., 2018). Copyright 2018, Springer Nature. d. Schematic of a bone marrow chip using subcutaneous implantation for producing engineered bone marrow (eBM). e. Bone marrow tissues before (0 week) and after 8 weeks of implantation. The chip enables media perfusion and the delivery of biochemical cues. Scale bars, 2 mm. d-e, Reproduced with permission (Torisawa et al., 2014). Copyright 2014, Springer Nature.
