Figure 2.
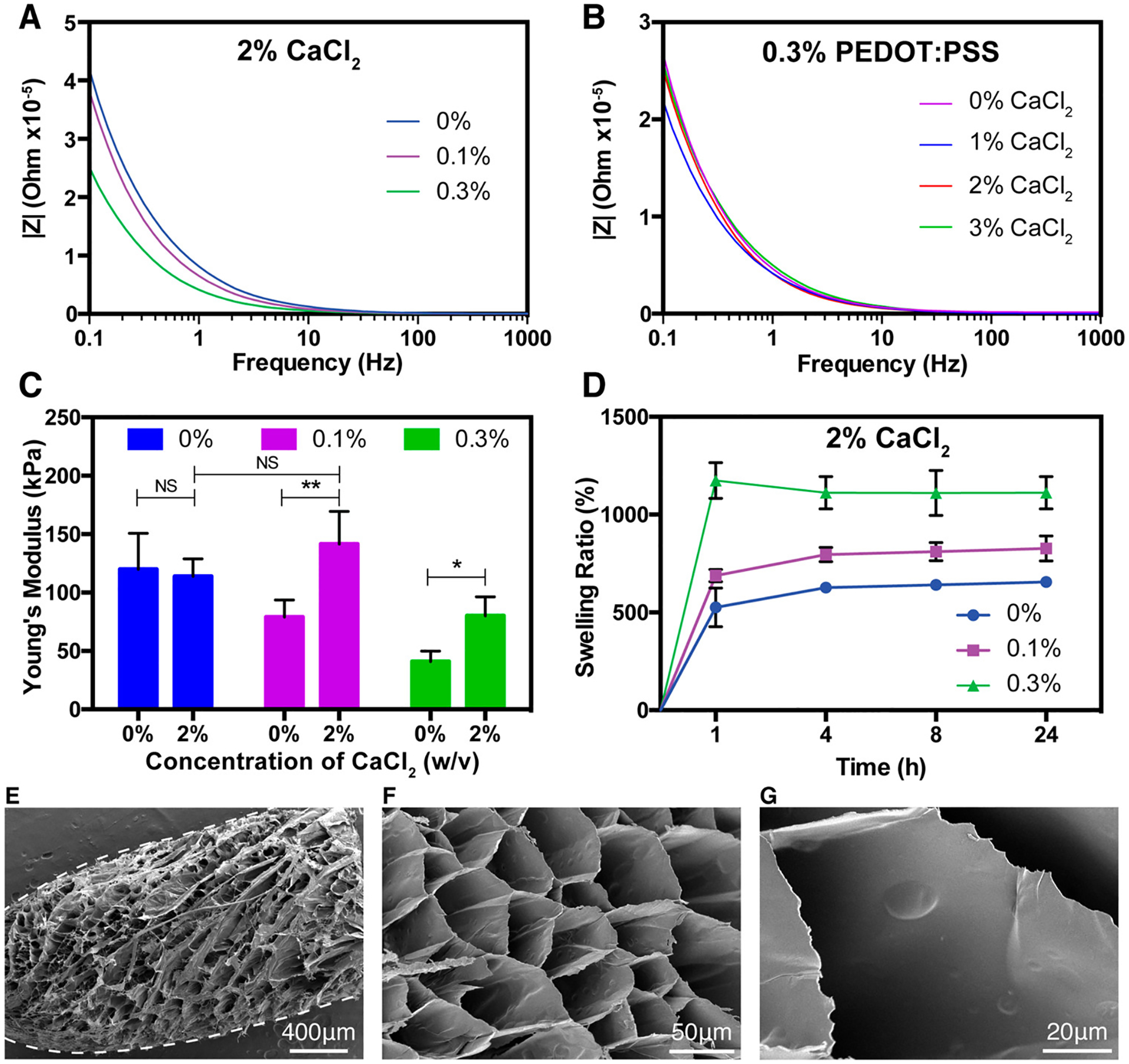
Physical and microstructural characterization of GelMA/PEDOT:PSS hydrogels. (A) EIS spectra of hydrogels cross-linked with 2% (w/v) calcium chloride containing varying concentrations of PEDOT:PSS. (B) EIS spectra of hydrogel samples containing 7% GelMA and 0.3% PEDOT:PSS, cross-linked with varied concentrations of calcium chloride. (C) Young’s modulus of hydrogels formed by using various concentrations of PEDOT:PSS, cross-linked with control PBS or 2% calcium chloride solution. (D) Swelling ratio of hydrogels with various concentrations of PEDOT:PSS cross-linked with 2% CaCl2 at different time points. Representative SEM images of (E) a whole fiber after swelling in DI water and lyophilization and (F) cross-section of a fiber formed by wet-spinning procedure with 7% GelMA, 0.3% PEDOT:PSS, and cross-linked with 2% CaCl2. (G) High magnification representative SEM image of a hydrogel showing the absence of large aggregated particles. (Data plotted as mean ± SD, * = p < 0.05; ** = p < 0.01).
