Fig. 4.
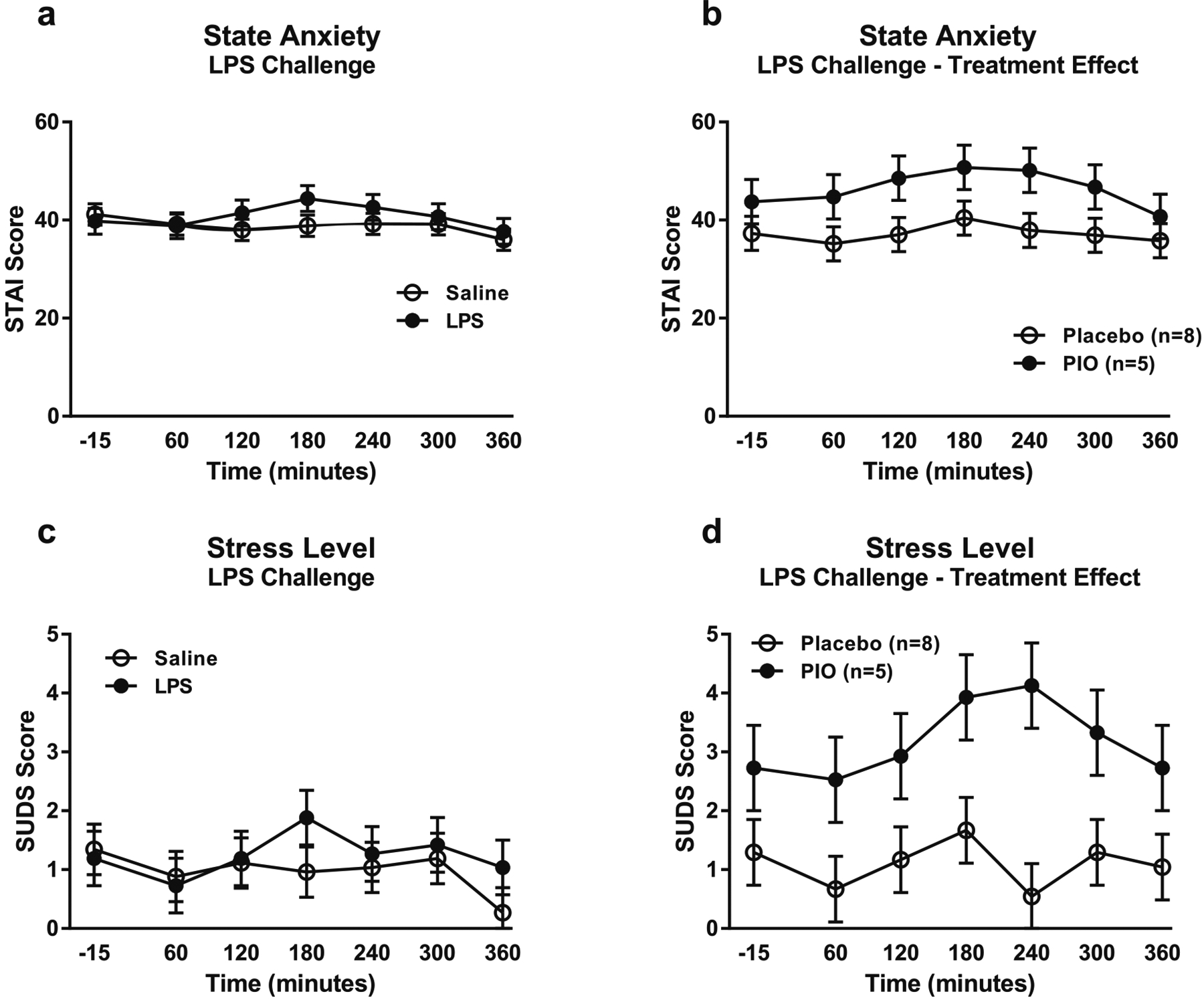
Anxiety and stress responses to the LPS challenge session. Data are mean ± SEM. a Effect of the LPS challenge on state anxiety, compared with saline (n = 13). Covariates in the model included alcohol dependence severity (ADS) score and baseline anxiety measured by the CPRS. b Effect of pioglitazone on anxiety response to the LPS challenge (pioglitazone: n = 5; placebo: n = 8). Covariates in the model included ADS score and baseline PACS craving score. c Effect of the LPS challenge on subjective stress level, compared with saline (n = 13). Covariates in the model included race, smoking status, ADS score, neuroticism score, years of education, and baseline CPRS anxiety. d Effect of pioglitazone on subjective stress response to the LPS challenge (pioglitazone: n = 5; placebo: n = 8). Covariates in the model included ADS score, neuroticism score, years of education, and baseline PACS craving score. For detailed statistics, see “Results”
