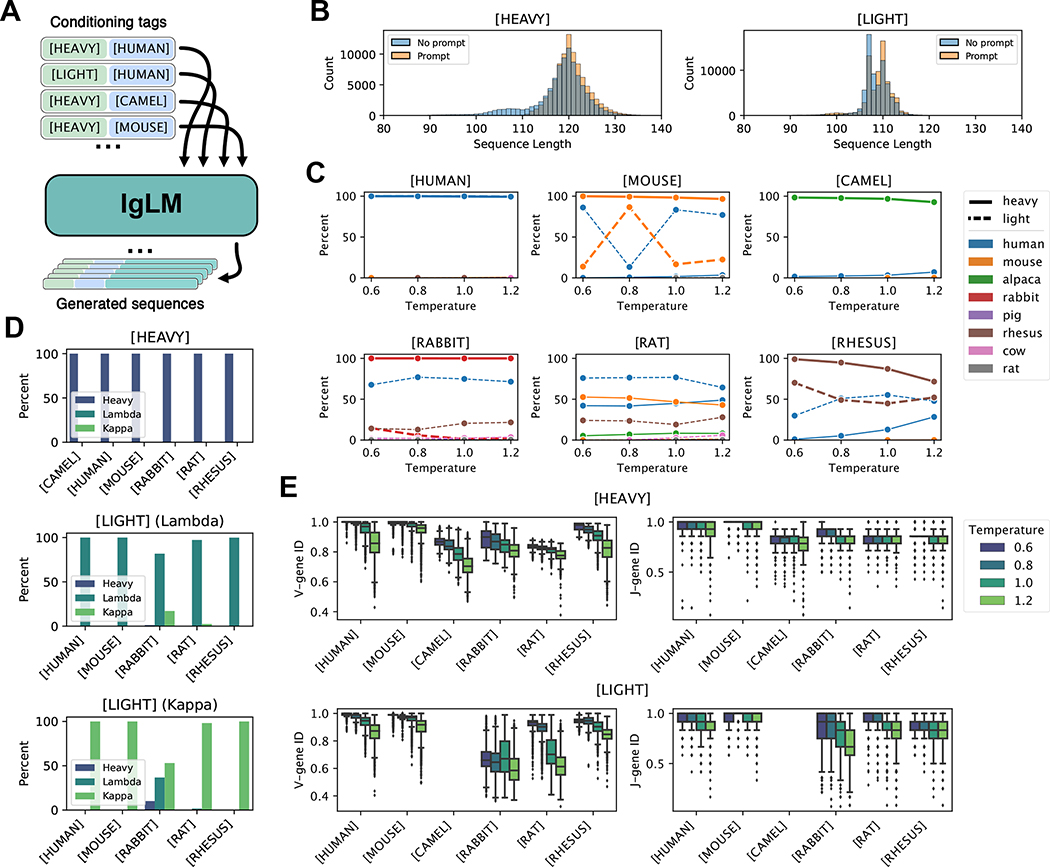
Figure 2.
Controllable antibody sequence generation. (A) Diagram of procedure for generating full-length antibody sequences given a desired species and chain type with IgLM. (B) Length of generated heavy and light with and without initial three residues provided (prompting). (C-E) Analysis of full-length generated sequences under different conditioning settings [n = 220,000]. (C) Adherence of generated sequences to species conditioning tags. Each plot shows the species classifications of antibody sequences generated with a particular species conditioning tag (indicated above plots). Solid and dashed lines correspond to sequences generated with heavy- and light-chain conditioning, respectively. (D) Adherence of generated sequences to chain conditioning tags. Top plot shows the percentage of heavy-chain-conditioned sequences classified as heavy chains, for each species conditioning tag. Lower plots show the percentage of light-chain-conditioned sequences, further divided by whether initial residues were characteristic of lambda or kappa chains, classified as lambda or kappa chains. (E) Effect of sampling temperature on germline identity for generated heavy and light chain sequences. As sampling temperature increases, generated sequences diverge from the closest germline V- and J-gene sequences.