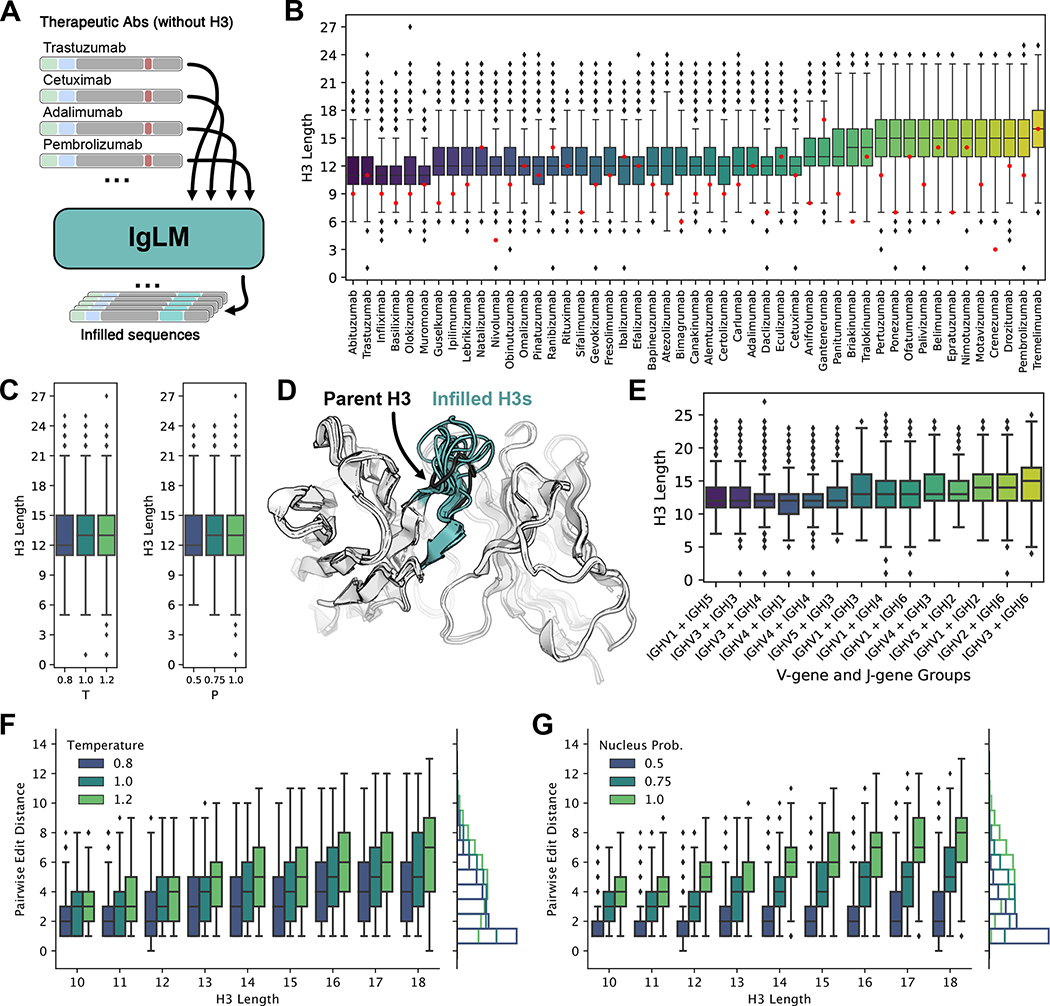
Figure 3.
Generation of infilled therapeutic antibody libraries. (A) Diagram of procedure for generating diverse antibody libraries by infilling the CDR H3 loops of therapeutic antibodies. (B) Distribution of infilled CDR H3 loop lengths for 49 therapeutic antibodies. Parent CDR H3 lengths are indicated in red. (C) Relationship between sampling temperature () and nucleus probability and length of infilled CDR H3 loops [n = 432,763]. (D) Infilled CDR H3 loops for trastuzumab therapeutic antibody adopt diverse lengths and conformations. Structures for infilled variants are predicted with IgFold [n = 432,763]. (E) Distribution of infilled CDR H3 loop lengths for therapeutic antibodies grouped by nearest germline gene groups [n = 432,763]. (F-G) Effect of sampling temperature () and nucleus probability (P) on diversity of infilled CDR H3 loops for lengths between 10 and 18 residues [n = 432,763]. Pairwise edit distance measures the minimum edits between each infilled loop to another in the same set of generated sequences (i.e., within the set of sequences produced with the same and parameters). For both parameters, less restrictive sampling produces greater infilled loop diversity.