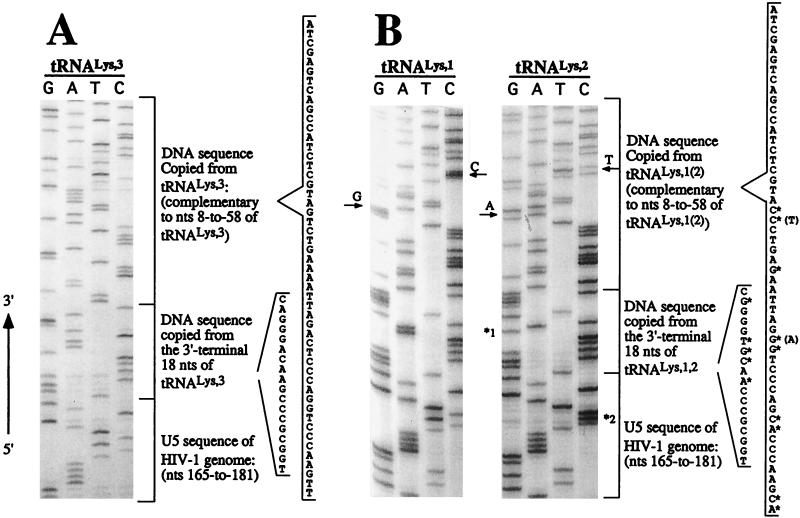
FIG. 2.
Analysis of tRNALys isoacceptors used to initiate the reverse transcription in HIV-1. Viruses produced from transfected 293T or infected SupT1 cells were used in an endogenous reverse transcription reaction. The products of this reaction were amplified by a PCR with P1 primer and Lys1,2,3 primer (Fig. 1). PCR products were cloned, and the DNA sequence was determined. The identities of tRNAs used as primers in the initiation of reverse transcription were determined by their DNA sequence and comparison to known sequences (24). (A) DNA sequence (in genomic RNA sense) copied from the 3′ end of tRNA3Lys and the first strong-stop DNA product (only partial U5 sequence is shown). (B) DNA sequence from the 3′ ends of tRNA1Lys and tRNA2Lys and extended strong-stop DNA products. The individual nucleotides with an asterisk shown in the sequence indicate the nucleotide differences between tRNA3Lys and tRNA1,2Lys. The 2-nt differences between tRNA1Lys and tRNA2Lys are indicated by arrows. *1 indicates an A-to-G mutation in tRNA2Lys-extended DNA; *2 indicates the T-to-C mutation. Either mutation was probably created by HIV-1 RT or Taq DNA polymerase during the endogenous RT-PCR.