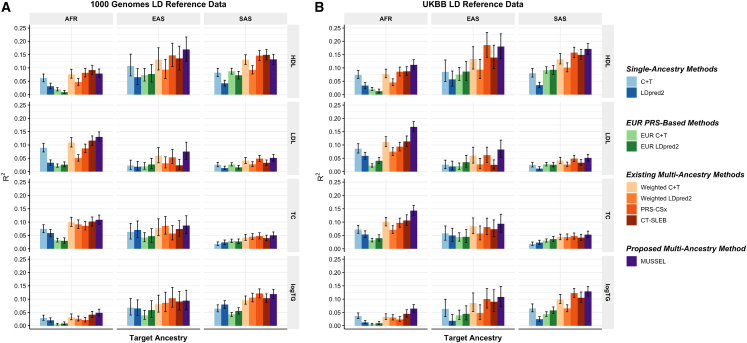
Figure 4.
Prediction R2 of the PRS trained based on GWAS summary data from GLGC on non-EUR validation individuals from UKBB
Discovery GWASs from GLGC include GWAS on EUR (NGWAS = 842,660–930,671), AFR or admixed AFR (NGWAS = 87,760–92,555), Hispanic/Latino (NGWAS = 46,040–49,582), EAS (NGWAS = 82,587–146,492), and SAS (NGWAS = 33,658–34,135). The validation dataset consists of individuals of EUR (N = 17,457–19,030), AFR (N = 7,954–8,598), EAS (N = 1,752–1,921), or SAS (N = 9,385–10,288) origin in UKBB. The LD reference data are from either (A) the 1000 Genomes Project (498 EUR, 659 AFR, 347 AMR, 503 EAS, and 487 SAS), or (B) UKBB data (PRS-CSx: default UKBB LD reference data which overlap with our testing samples including 375,120 EUR, 7,507 AFR, 687 AMR, 2,181 EAS, and 8,412 SAS; all other methods: UKBB tuning samples including 10,000 EUR, 4,585 AFR, 1,010 EAS, and 5,427 SAS). The ancestry of UKBB individuals was determined by a genetic ancestry prediction approach (supplemental information). Due to the low prediction accuracy of genetic component analysis and extremely small validation sample size of UKBB AMR, prediction R2 on UKBB AMR is unreliable and thus is not reported here. All methods were evaluated on the ∼2.0 million SNPs that are available in HapMap 3 + MEGA, except for PRS-CSx, which is evaluated based on the HapMap 3 SNPs only, as implemented in their software. Ancestry- and trait-specific GWAS sample sizes, number of SNPs included, and validation sample sizes are summarized in Table S10. A random half of the validation individuals is used as the tuning set to tune model parameters as well as train the SL in CT-SLEB and MUSSEL or the linear combination model in weighted LDpred2, PRS-CSx, and weighted MUSS. The other half of the validation set is used as the testing set to report R2 values and the corresponding 95% bootstrap CIs for each ancestry, after adjusting for age, sex, and the top ten genetic principal components. In (B), PRS-CSx and other methods do not have a fair comparison because the UKBB LD reference data provided by the PRS-CSx software (UKBBPRS-CSx) is much larger than that for other methods, and thus the R2 of PRS-CSx PRS may be inflated due to a large overlap between UKBBPRS-CSx and the UKBB testing sample. Detailed results are reported in Table S17.