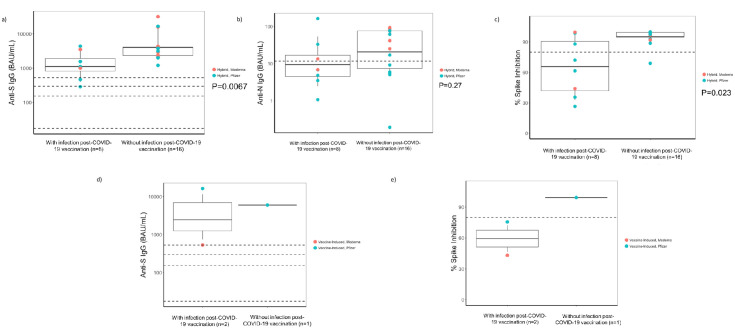
Fig 5. Immune responses in nursing home participants with and without infection post-COVID-19 vaccination—Georgia, December 2020–July 2022.
A: Distribution of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S) IgG among the hybrid immunity in nursing home residents with and without infection post-COVID-19 vaccination (n = 24). anti-S IgG: anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike IgG; BAU/mL: Binding antibody units/mL. Footnotes: Y-axis: Antibody levels in BAU/mL in logarithmic scale. To evaluate infections post-COVID-19 vaccination, observations of mean antibody titer values from participants who developed infection ≥14 days postvaccination were compared with observations from participants who did not develop an infection post-COVID-19 vaccination by performing a t-test; a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Matching was done on the type of exposure and serology collected at a similar time point within a 7-day window. The p = 0.0067 was statistically significant. B: Distribution of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid (N) IgG antibodies among the hybrid immunity in nursing home residents with and without infections post-COVID-19 vaccination (n = 24). anti-N IgG: anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid IgG; BAU/mL: Binding antibody units/mL. Y-axis: Antibody levels in BAU/mL in logarithmic scale. Footnote: To evaluate infections post-COVID-19 vaccination, observations of mean antibody titer values from participants who developed infection ≥14 days postvaccination were compared with observations from participants who did not develop an infection post-COVID-19 vaccination by performing a t-test; a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Matching was done on the type of exposure and serology collected at a similar time point within a 7-day window. The p = 0.27 was not statistically significant. C: Virus neutralizing capacity among the hybrid immunity in nursing home residents with and without infections post-COVID-19 vaccination (n = 24). Virus neutralizing capacity = percent spike inhibition; Y axis in %. Footnote: To evaluate infections post-COVID-19 vaccination, observations of mean antibody titer values from participants who developed infection ≥14 days postvaccination were compared with observations from participants who did not develop an infection post-COVID-19 vaccination by performing a t-test; a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Matching was done on the type of exposure and serology collected at a similar time point within a 7-day window. The p = 0.023 was not significant. D: Distribution of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S) IgG among the vaccine-induced immunity in nursing home residents with and without infections post-COVID-19 vaccination (n = 3). Footnote: anti-S IgG: anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike IgG; BAU/mL: Binding antibody units/mL. Y-axis: Antibody levels in BAU/mL in logarithmic scale. To evaluate infections post-COVID-19 vaccination, observations of mean antibody titer values from participants who developed infection ≥14 days postvaccination were compared with observations from participants who did not develop an infection post-COVID-19 vaccination by performing a t-test; a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Matching was done on the type of exposure and serology collected at a similar time point within a 7-day window. We were unable to assess statistically due to small numbers; hence, no p- values are provided. E: Virus neutralizing capacity among the vaccine-induced residents, comparing those with and without infection post-COVID-19 vaccination (n = 3). Footnote: Virus neutralizing capacity = percent spike inhibition; Y axis in %. To evaluate infections post-COVID-19 vaccination, observations of mean antibody titer values from participants who developed infection ≥14 days postvaccination were compared with observations from participants who did not develop a post-COVID-19 vaccination infection by performing a t-test; a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Matching was done on the type of exposure and serology collected at a similar time point within a 7-day window. We were unable to assess statistically due to small numbers; hence, no p- values are provided.