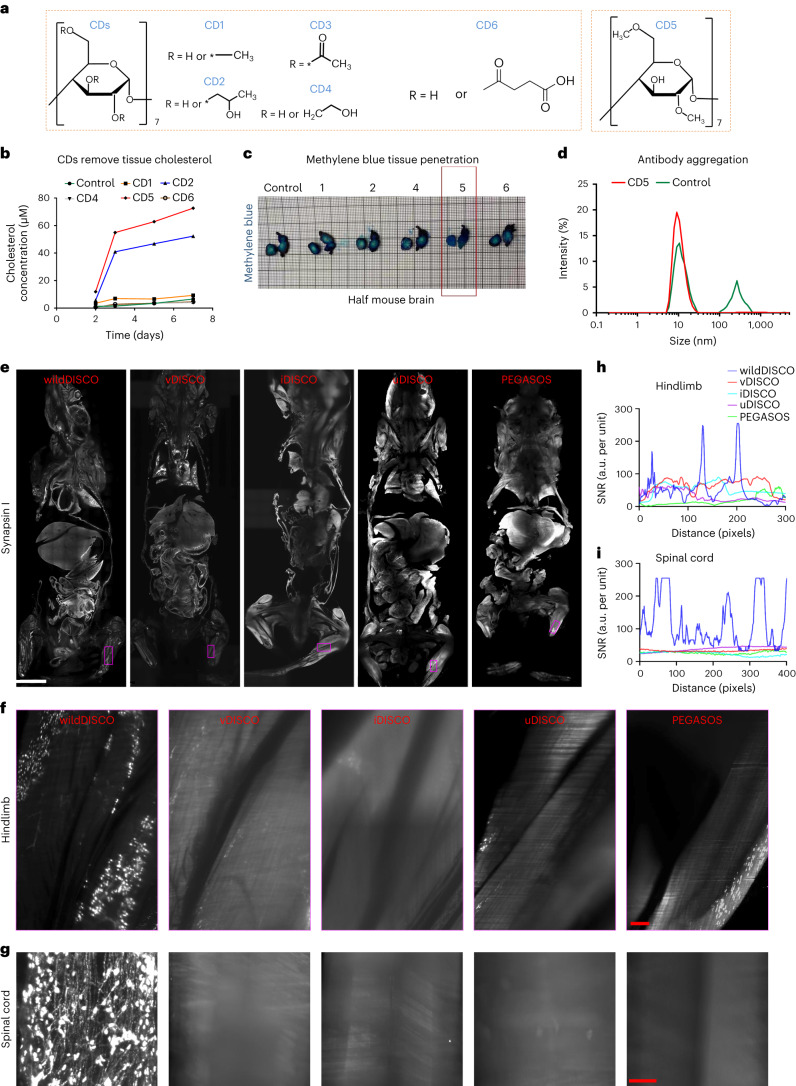
Fig. 1. Exploring cyclodextrins as whole-body conventional IgG antibody staining chemicals and comparison of different clearing methods for whole mouse antibody staining.
a, The structure of cyclodextrin (CD) with different substituent groups: CD1 (methyl-β-cyclodextrin), CD2 (2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin), CD3 (triacetyl-β-cyclodextrin), CD4 ((2-hydroxyethyl)-β-cyclodextrin), CD5 (heptakis(2,6-di-O-methyl)-β-cyclodextrin) and CD6 (succinyl-β-cyclodextrin). b, Measurements of supernatant cholesterol concentration after different CD-containing buffer incubation on the seventh day for 25 mg mouse liver sections. c, Methylene blue staining of a single hemisphere of mouse brains after permeabilization with different CD-containing solutions. CD5 is shown to greatly enhance tissue permeabilization compared to others. d, DLS for size distribution of TH antibody in solutions with and without CD5. e–i, Comparison of different clearing methods for whole mouse body antibody staining. e, Optical 2D light-sheet microscopy images of the whole mouse body stained with synapsin 1 antibody by wildDISCO, vDISCO, iDISCO, uDISCO and PEGASOS methods, respectively. Scale bar, 5,000 μm. f,g, Representative 2D optical images of mouse hindlimb (f) and spinal cord (g) by wildDISCO, vDISCO, iDISCO, uDISCO and PEGASOS methods. Scale bars: f, 200 μm; g, 300 μm. n = 3. h,i, Quantification of antibody penetration depth into the hindlimb (h) and spinal cord (i) of mice by wildDISCO, vDISCO, iDISCO, uDISCO and PEGASOS methods.