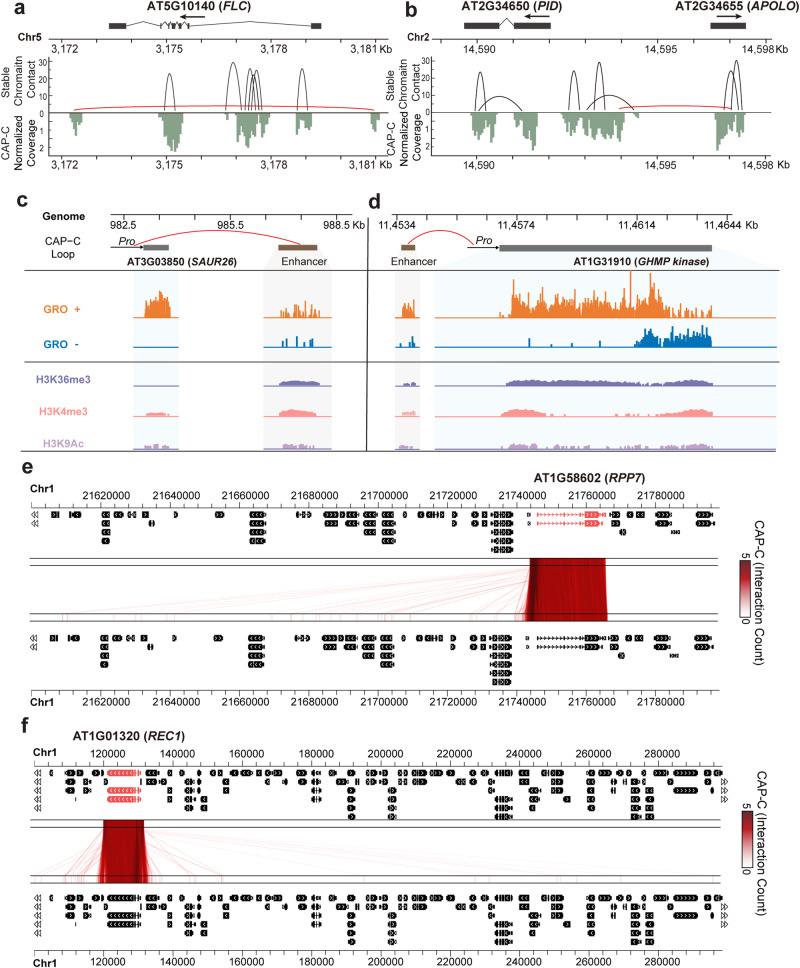
Fig. 2. Characterization of chromatin conformations.
a, b The stable chromatin contacts around FLC (a) and PID and APOLO (b) loci. The schematic gene structure was aligned to stable chromatin contacts (loops) captured by CAP-C and coverage results, with boxes representing exons and lines representing introns. The red curve shows the reported chromatin contacts validated experimentally, and the black curves show the newly identified stable chromatin contacts by CAP-C, associated with which are the CAP-C reads shown under the chromatin contacts. c, d Representative examples demonstrating enhancer-promoter interactions. Black boxes represent gene loci, arrows show the promoter regions and transcription directions. Brown boxes represent active enhancer loci. Interactions between an enhancer and a promoter are shown in the red curve. GRO-seq reads (GRO+ represents the sense strand, while GRO− represents the antisense strand) and the corresponding histone ChIP-seq tracks (H3K36me3, H3K4me3, H3K9Ac) were shown underneath each enhancer and gene locus. GIVE plots showing representative short-range (e, RPP7) and long-range (f, REC) intra-chromosomal DNA-DNA interactions based on our CAP-C data under normal growth conditions. To depict interactions, the chromosomes were plotted horizontally twice, producing a top and a bottom track. Each red line represents a chromatin contact, with the color scale indicating the strength of the contacts. The black boxes and lines indicate genes on the chromosomes.