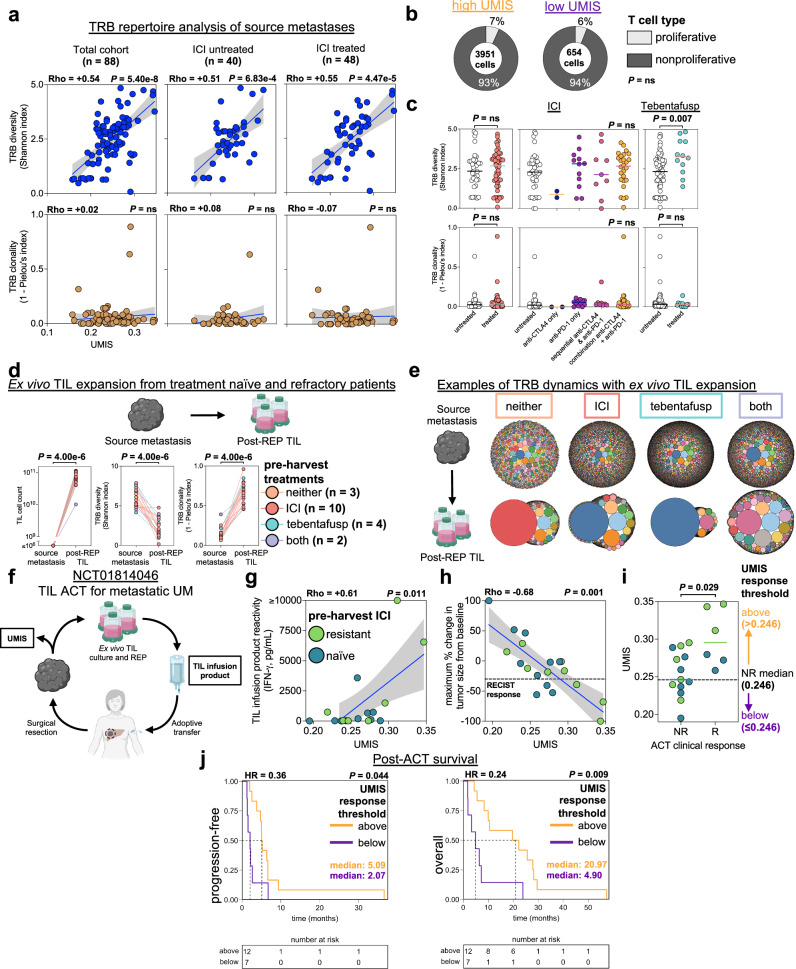
Fig. 6. UMIS identifies quiescent TIL resistant to ICI and tebentafusp but sensitive to ex vivo expansion and adoptive transfer.
a T cell receptor beta (TRB) repertoire analysis of bulk RNAseq of UM metastases (n = 88). Immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) refers to treatment history prior to metastatic biopsy. b Proportion of proliferative T cells in UMIS groups by single cell atlas. c Comparisons of TRB diversity and clonality in ICI or tebentafusp untreated versus treated metastases (ICI: 48 treated, 40 untreated; tebentafusp: 12 treated, 76 untreated). d Ex vivo TIL expansion from treatment naïve and refractory patients (n = 19). Listed therapies were received prior to metastatic biopsy. Changes in TIL cell counts (left), T cell receptor beta (TRB) diversity (middle), and TRB clonality (right) are shown for source metastases and corresponding TIL cultures post rapid expansion protocol (post-REP TIL). Metastases’ TIL counts were conservatively estimated to be ≤106. TRB repertoires were characterized with targeted TCR repertoire analysis. Schematic created with BioRender.com. e Examples of TRB dynamics with ex vivo TIL expansion. Bubble plots represent unique TRB clonotypes (color coded) with bubble size indicating percentage of total clonotypes. Shown are representative examples for each pre-harvest treatment group (neither = UM #73, ICI = UM #50, tebentafusp = UM #59, both = UM #49). Schematic created with BioRender.com. f Schematic for evaluation of UMIS in the context of NCT01814046 (ACT of TIL for metastatic UM)15. Created with BioRender.com. g Correlation of source metastasis UMIS with TIL infusion product reactivity (n = 17). h Correlation of source metastasis UMIS with maximum percent change in tumor size from baseline (RECIST v1.1) after TIL ACT. RECIST response line is drawn at −30% (n = 19). i Comparison of UMIS between responders (R; n = 6) and nonresponders (NR; n = 13) to TIL ACT. The median UMIS of the NR group (0.246) was used as a clinical response threshold for outcome analyses. j Time-to-event curves of post-ACT survivals by UMIS response thresholds (n = 19). Progression-free survival used progressive disease as the event (median follow-up (months): high = 5.09, low = 2.07). Overall survival used death as the event (median follow-up (months): high = 20.97, low = 4.90). Hazard ratios (HR) are for above versus below threshold groups. Statistical comparisons were performed using Spearman’s rank correlation with overlaid simple linear regression to illustrate linearity (a, g, h), Fishers exact test (b), Wilcoxon rank-sum test (two-tailed) (c, i), Kruskal–Wallis test by ranks (c), Wilcoxon signed-rank test (two-tailed) (d) or logrank test (j).