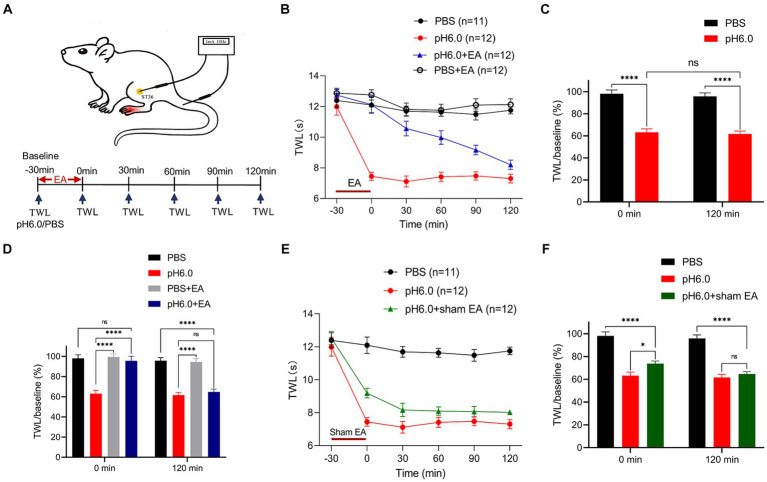
Figure 1.
Electroacupuncture (EA) stimulation had an analgesic effect on pH 6.0-induced pain as measured in the left hind paw of rats. (A) Schematic diagrams showing the location of the “Zusanli” acupoint (ST36) and EA treatment in the rat, as well as the experimental timeline. (B) Time-dependent changes of thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) values after the application of normal or pH 6.0 phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) into the left hind paw and accompanying EA stimulation at ST36. Ratios of TWL values measured at the indicated times and at baseline (−30 min; TWL/baseline) at the 0- and 120-min time points without (C) and with EA (D). (E) Time-dependent changes of the TWL values after sham EA stimulation. (F) TWL/baseline ratios at the 0-min and 120-min time points after sham EA stimulation. In this and in all further Figs, means ± S.E.M. values were calculated from measurements made in the indicated number of animals, as shown in brackets. *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001.