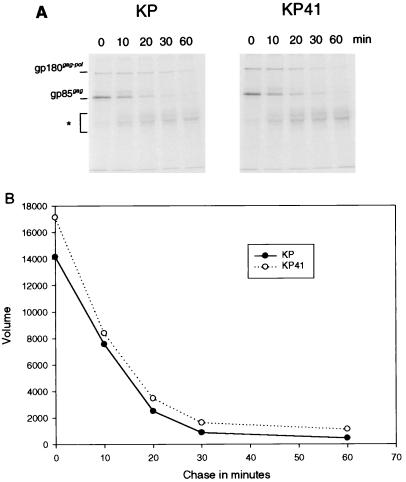
FIG. 4.
Pulse-chase analysis of gp85gag, the precursor of glycosylated Gag encoded by KP and KP41. M. dunni cells chronically infected with KP or KP41 were pulsed with [35S]methionine-cysteine for 10 min and chased in medium without radioisotope for 0 to 60 min before cell lysis. Lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with a rabbit antiserum to the N-terminal peptide 4210 of the glycosylated Gag cytoplasmic tail (29) and separation by SDS-PAGE (A). After the 10-min pulse (time zero), two proteins were labeled: gp85gag and gPr180gag-pol, which is a glycosylated gag-pol fusion protein (13). After 10 min of chase, two additional protein appeared: one slightly larger than gp85gag, which is likely a proteolytic cleavage product of gPr180gag-pol, and a diffuse protein ranging from 40 to 55 kDa (∗), which is the N-terminal cleavage product of gp85gag (15). (B) Quantification of the gp85gag bands for KP and KP41. The vertical axis represents arbitrary units of the volume measurements on a PhosphorImager.