Extended Data Fig. 6 |. Multiple sequence alignment of ATG16 proteins, and atg-16.2 mRNA expression levels in C. elegans.
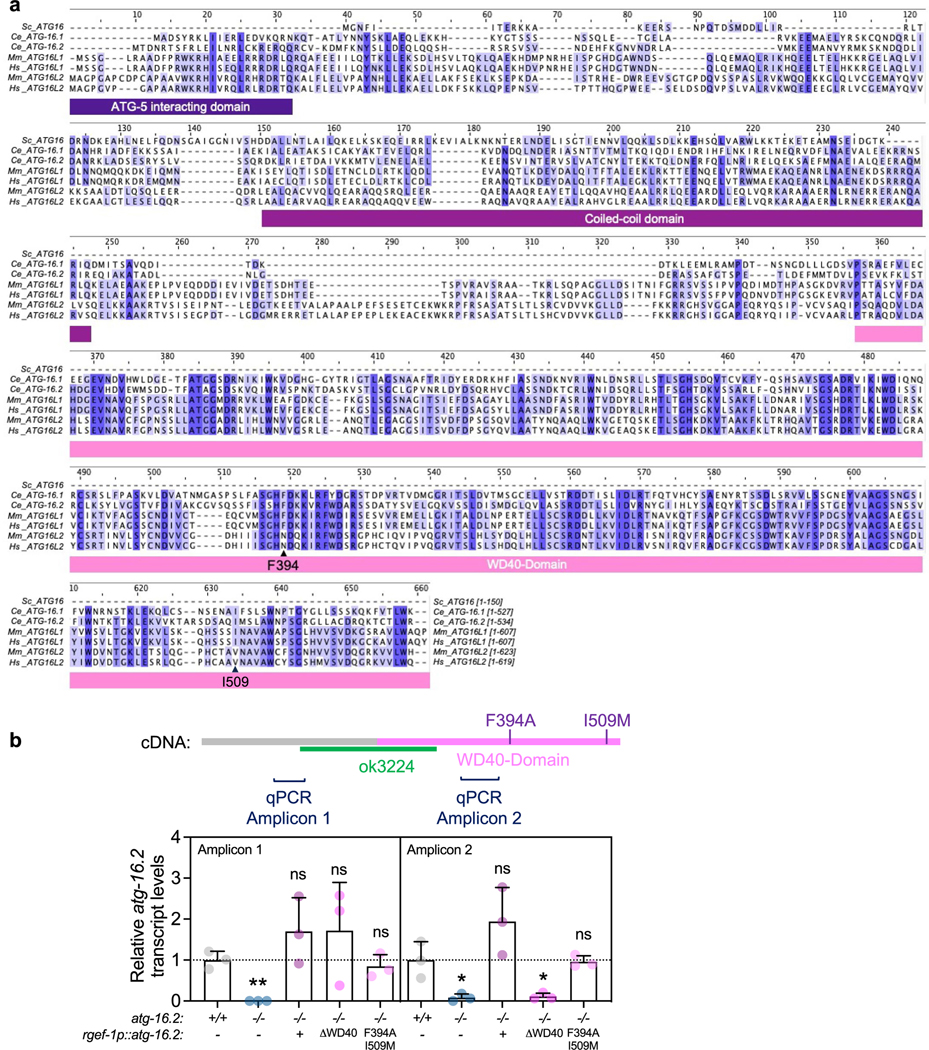
(a) Primary sequences of ATG16 proteins from S. cerevisiae (1 isoform, Sc_ATG16), C. elegans (2 isoforms, Ce_ATG-16.1, Ce_ATG-16.2), Mus musculus (2 isoforms, Mm_ATG16L1, MmATG16L2), and humans (2 isoforms, Hs_ATG16L1, Hs_ATG16L2) were aligned by the Clustal Omega and colored by conservation with darker shades indicated increased conservation ( Jalview). Protein elements of ATG16 proteins are drawn under the alignment and phenylalanine 349 and isoleucine 509 are indicated with an arrow. Sequences showed are ATG16 (NP_013882.1) in S. cerevisiae, ATG16.2 (NP_495299.2) in C. elegans, ATG16 (NP_001138124.2) in D. melanogaster, ATG16L1 (NP_001192320.1) in M. musculus, and ATG16L1 (NP_001350671.1) in H. sapiens. (b) Transcript levels of atg-16.2 in wild-type (WT), atg-16.2(ok3224), and atg-16.2(ok3224) animals expressing full-length atg-16.2, atg-16.2(ΔWD40), or atg-16.2(Phe394A, Ile509Met) from the neuronal rgef-1 promoter. Schematic of atg-16.2 cDNA indicates the ok3224 deletion, the WD40 domain, the position of the Phe394Ala and Ile509Met point mutations, and the amplicons produced by the primers used in this experiment. Data are the mean and s.e.m. of three biological replicates, each with three technical replicates, and are normalized to the mean expression levels of three housekeeping genes. Amplicon 1: **P = 0.0013, ns P = 0.23, P = 0.36, P = 0.49, Amplicon 2: *P = 0.03, ns P = 0.16, *P = 0.03, ns P = 0.89 by unpaired two-sided t-test with control.
