Fig. 3. Chimerism and CBC after CKBMT differ on the basis of conditioning regimen.
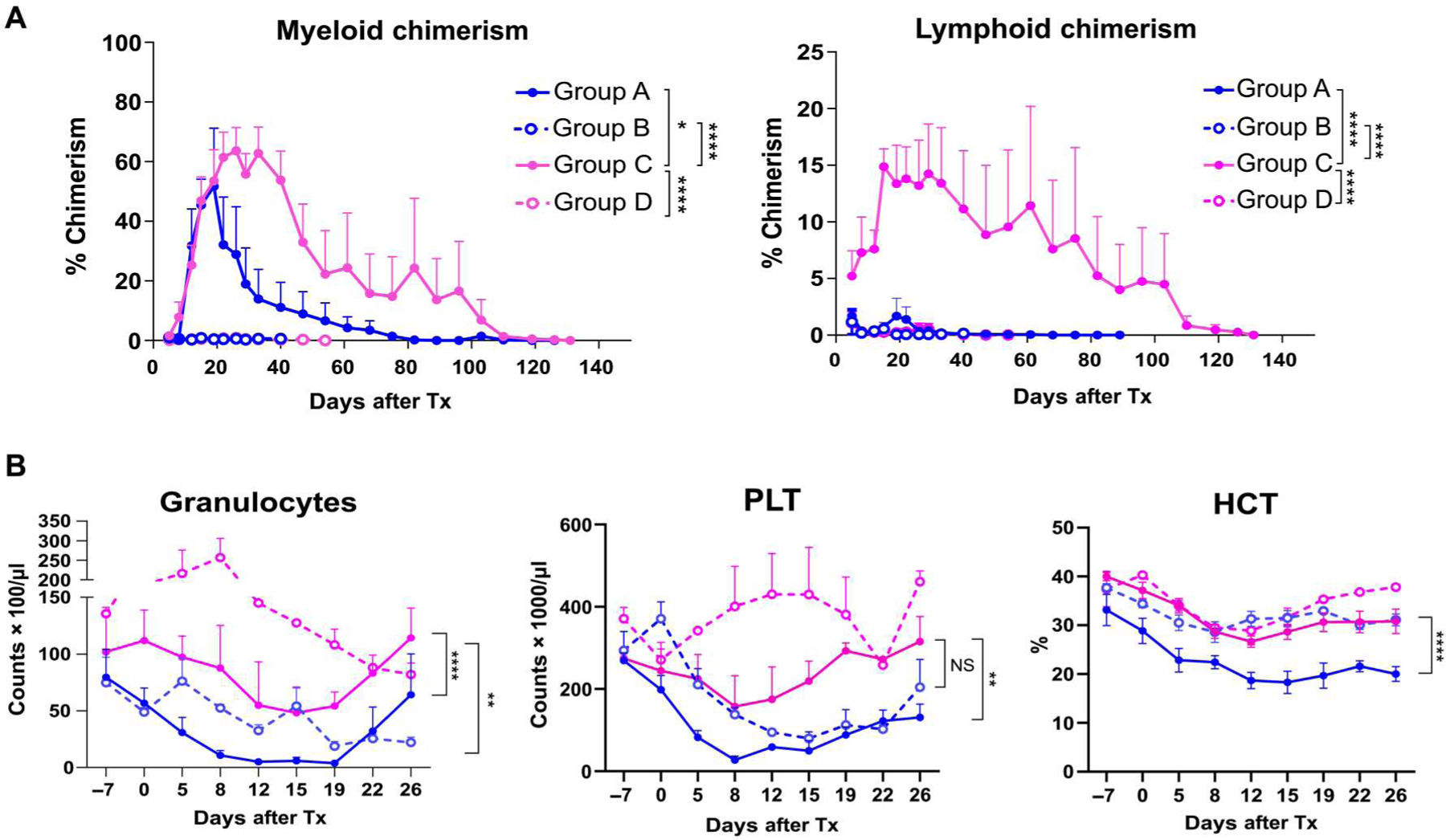
(A) Hematopoietic chimerism after CKBMT. Peripheral blood chimerism was determined by flow cytometry using H38 expression. Both myeloid (left) and lymphoid (right) chimerism were measured (n = 6, group A; n = 3, group B; n = 6, group C; n = 2, group D; each sample was obtained from different NHPs). (B) CBC after CKBMT. Granulocytes, platelets (PLT), and hematocrit (HCT) were measured for groups A, B, C, and D (n = 6, group A; n = 4, group B; n = 6, group C; n = 2, group D; each sample was obtained from different NHPs). Mixed-model ANOVA for repeated measure was used for data analysis. Data are presented as means ± SE. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001.
