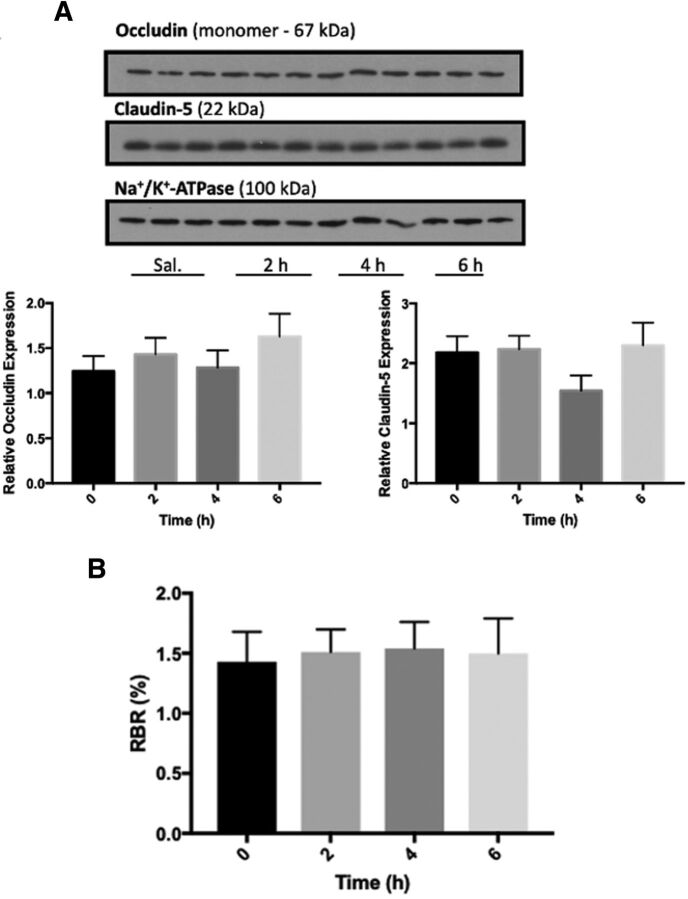
Fig. 12.
BMP-9 Treatment does not alter BBB expression of critical tight junction proteins or paracellular permeability in rat brain microvessels. (A) Animals were administered a single dose of BMP-9 (1 μg/kg, i.p.). After the time course of 2 to 6 hours, animals were euthanized and brain microvessels were isolated for western blot analysis. Isolated microvessels (10 μg) were resolved on a 4%–12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and analyzed for expression of claudin-5 and occludin monomers. Relative levels of claudin-5 and occludin monomers were determined by densitometric analysis and normalized to sodium-potassium ATPase. Western blot data are reported as mean ±S.D. of three independent experiments where each treatment group consisted of three individual animals (n = 3). Asterisks represent data points that were significantly different from control (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01). (B) Animals were administered a single dose of BMP-9 (1 μg/kg, i.p.). After 2 to 6 hours BMP-9 exposure, paracellular permeability to [14C]sucrose, a vascular marker that does not typically cross the BBB, was measured by in situ brain perfusion. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. of six animals per time point. Asterisks represent data points that were significantly different from control animals (*p < 0.05; **p< 0.01).