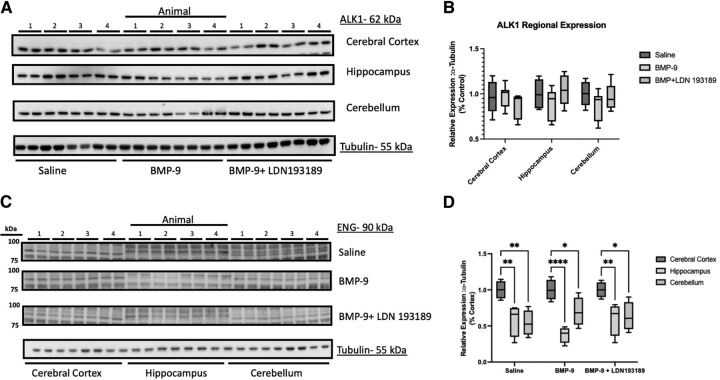
Fig. 6.
Expression of ALK1 receptors and ENG in cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum after treatment with BMP-9. (A) Animals were administered a single dose of BMP-9 (1.0 μg/ml) or LDN193189 (10 mg/kg) at 1 hour prior to receiving a single dose of BMP-9 (1.0 μg/ml). After 6 hours, animals were euthanized and brain microvessels isolated and prepared for western blot analysis. Isolated microvessels (10 μg) were resolved on a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane, and analyzed for expression of ALK1 or tubulin (i.e., the loading control). Each lane pair on the depicted western blot corresponds to a microvessel sample obtained from a single experimental animal. (B) Relative levels of ALK1 protein expression were determined by densitometric analysis and normalized to tubulin. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. from at least two independent blots, where each treatment group consisted of normalized data from eight individual animals (n = 8). (C) Isolated microvessels (10 μg) were resolved on a 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane, and analyzed for expression of ENG or tubulin (i.e., the loading control). Each lane pair on the depicted western blot corresponds to a microvessel sample obtained from a single experimental animal. (D): Relative levels of ENG protein expression were determined by densitometric analysis and normalized to tubulin. Results are expressed as mean ± S.D. where each treatment group consisted of normalized data from four individual animals (n = 4). Asterisks represent data points that were significantly different from control (**p < 0.01).