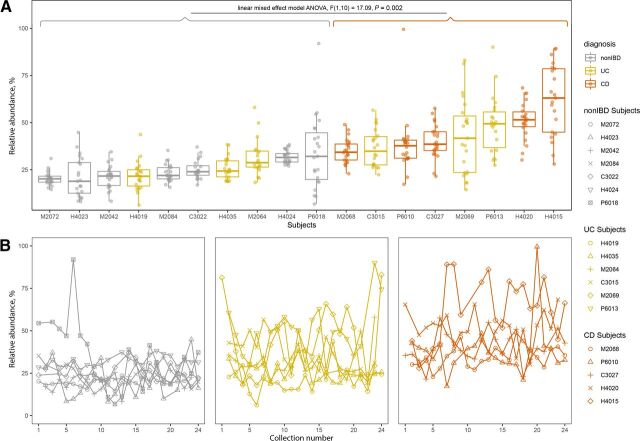
Fig. 5.
Known and putative azo-reducing species are more abundant in the IBD gut. Relative abundance of known and putative azo-reducing species in HMP2 subjects with more than 20 total stool collections. (A) Relative abundance of known and putative azo-reducing species for qualifying participants across non-IBD, UC, and CD populations. Subjects with CD have significantly higher relative abundances of known+putative azo-reducing species than healthy subjects (non-IBD) per linear mixed-effects model ANOVA, F(1,10) = 17.09, P < 0.003. (B) Relative abundance of putative azo-reducing species over time for healthy (non-IBD), UC, and CD participants. Each line represents a single participant, and each point is the summed relative abundance of known+putative azo-reducing species at that collection point. The key on the right links relative abundance distributions for each subject with the same data point shown over collection numbers. Collections were taken approximately every 14 days.