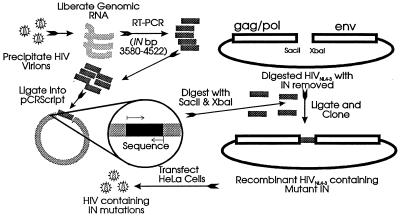
FIG. 2.
Cloning strategy for analyzing mutations in integrase. The diagram illustrates the general cloning scheme designed to insert integrases from drug-resistant organisms into the wild-type HIVNL4-3 background. Briefly, RNA was isolated from virions and subjected to RT-PCR with primers that introduced silent mutations (SacII and XbaI sites) upstream and downstream of the integrase gene. These RT-PCR products were ligated into pCR-Script for sequencing. Clones containing mutant integrases were digested with SacII and XbaI, and the integrase gene was ligated into a similarly digested HIVNL4-3 plasmid, allowing the entire integrase gene, and only the integrase gene, to be switched into a drug-sensitive HIVNL4-3 background.