Figure 2.
Structural modeling of SEPHS1
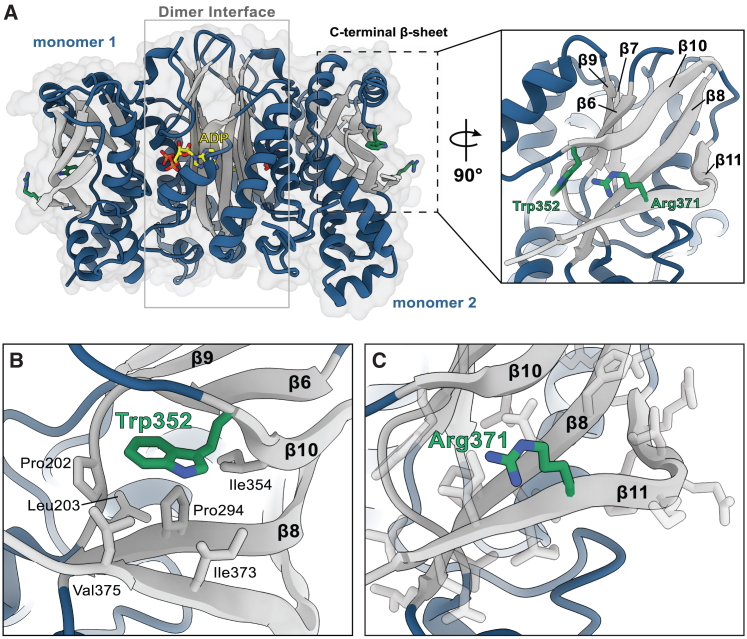
(A) Overall structural organization of SEPHS1 (PDB: 3FD6). Interactions between the N-terminal regions of monomers 1 and 2 form a β-barrel-like structure to stabilize the homodimer and active sites. ADP is shown in yellow. Residues Trp352 and Arg371 are situated in the C-terminal β-sheet and are highlighted in green.
(B) Trp352 resides in a hydrophobic pocket stabilized by interactions with neighboring hydrophobic residues.
(C) Arg371 is located on the solvent-exposed face of β11 and does not appear to form any significant interactions with surrounding residues. All modeling was performed using PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0 Schrödinger, LLC).