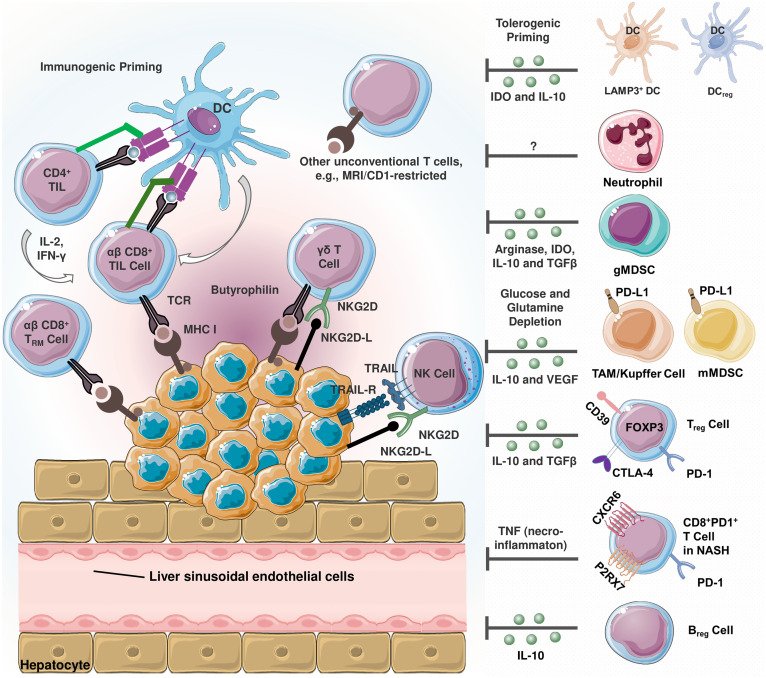
Figure 1.
Schematization of infiltrating immune cells in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (20). Immunosuppressive and immunostimulatory cells coexist in the tumor microenvironment (TME). HCC cells express TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor (21). TRAIL promotes natural killer (NK) cell infiltration into the TME, and TRAIL-expressing NK cells exert apoptotic effects on HCC cells. The activating cell surface receptor NKG2D is predominantly found on the surface of cytotoxic immune cells, and its ligands can be expressed in virtually all cell types upon induction including oncogenic transformation (22). Tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells recognize cancer cells via peptide- major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) complexes. Once recognized, malignant cells are eliminated via perforin- or FAS-dependent mechanisms. MHC I expression is critical since cancer cells lacking MHC I expression can only be eliminated by NK cells (23). In terms of tolerogenic signaling, regulatory dendritic cells (DCreg) are involved in T cell polarization, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and T regulatory cell (Treg) differentiation and activity (24). Similarly, lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 3 (LAMP3)+ dendritic cells (DCs) are positively correlated with the infiltration of exhausted CD8+ T cells and Tregs (25). In TME, MDSCs are reported to promote tumor progression and are correlated with poor prognosis (26). These cells induce immunosuppression by secreting arginase-1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), TGF-β and interleukin-10 (IL-10) (27). Being a significant source of the latter, regulatory cells (Breg) also secrete IL-10 (20). Kupffer cells and other tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) are involved in hepatocarcinogenesis and immune evasion in different mechanisms including secreting immunosuppressive mediators, expressing programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), recruiting Tregs as well as IL-17-expressing CD4+ T helper 17 (Th17), and downregulating MHC II expression along with costimulatory molecules (20). In non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a subset of activated CD8+ T expressing exhaustion marker PD-1 are elevated (28). These cells exert an auto-aggressive behavior and drive necro-inflammation by secreting tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α).