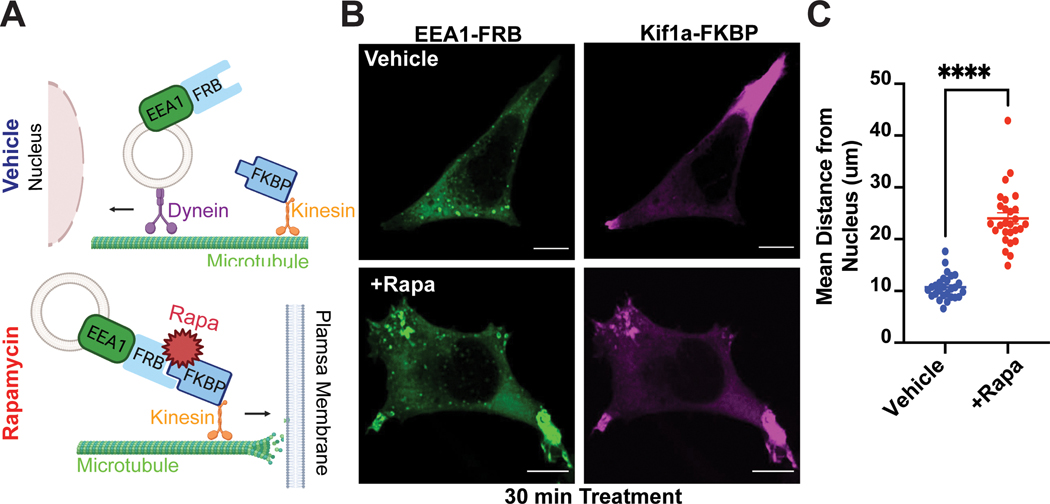
Figure 1. CID approach for redirecting endosomes.
A. Schematic of the approach. B-C. Rapid redistribution of early endosomes by rapamycin treatment. B. FRB-EEA1 (green), localized at early endosomes, and Kif1a-FKBP (magenta), localized near the cell periphery, visualized by immunofluorescence microscopy in fixed cells. In ethanol-treated cells (vehicle, top), early endosomes are dispersed in the cell. After 1μM rapamycin treatment for 30 min (bottom), early endosomes redistribute to the cell periphery. C. Increase in mean endosome distance from the nucleus in rapamycin-treated cells. Mean endosome distance per cell = 10.75μm ± 0.46 (EtOH) and 24.04μm ± 1.08 (rapamycin). Data are average from n = 3 biologically independent replicates ± s.e.m.; 27 cells total/condition; **** = p < 0.0001 by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bar = 10μm.