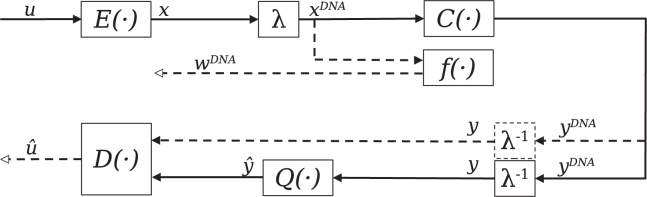
Figure 1.
Overview of the main components of Autoturbo-DNA: A given binary input u is encoded using the encoder network and subsequently mapped to a DNA sequence by the mapping function λ
The output of the mapping function is then modified by the channel simulator and optional evaluated for constraint adherence by the function . The output score of the evaluation function can be used as an additional loss metric for the encoder. The inverse of the mapping function translates the DNA sequence back into a binary representation y. Depending on the training stage and chosen configuration, the channel output is either directly decoded by the decoder function or first transcoded using the indel reduction component , and the resulting sequence is decoded by the decoder function, producing the binary output sequence .