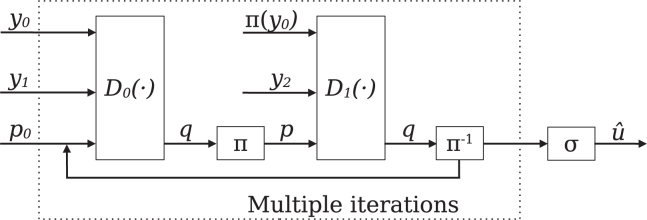
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration of the decoder, shown for rate
The input sequence y is split into the subsequences , and , which correspond to the encoded subsequences , and , respectively. and , together with a prior , are used as the input for the first decoder network . The output posterior q and are subsequently interleaved and serve, together with , as the input for the second decoder . The output of the second decoder is deinterleaved by the inverse of the interleaving function, , and is used as updated prior for the first decoder. This process will be repeated until a user-defined amount of iterations is reached. The final, deinterleaved output of the second decoder will then be used to generate the output sequence by a sigmoid activation function σ.