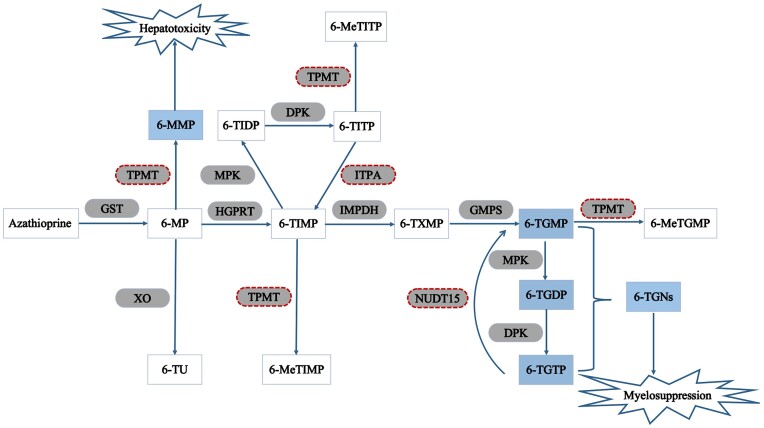
Figure 2.
The metabolic pathways of azathioprine. Azathioprine changes into 6-mercaptopurine after absorption by the GI tract. 6-mercaptopurine can then be metabolized through three competing pathways: conversion into 6-TIMP by HGPRT; methylation by TPMT into 6-MMP; and conversion into 6-TU by XO. 6-TIMP can then be successively metabolized into 6-TXMP and 6-TGNs by IMPDH and GMPS, respectively. GST: glutathione s-transferase; 6-MP: 6-mercaptopurine; TPMT: thiopurine s-methyltransferase; 6-MMP: 6-methylmercaptopurine; XO: xanthine oxidase; 6-TU: 6-thiouric acid; HGPRT: hypoxanthine–guanine phosphoribosyl transferase; 6-TIMP: 6-thioinosine monophosphate; MPK: monophosphate kinase; 6-TIDP: 6-thioinosine diphosphate; DPK: diphosphate kinase; 6-TITP: 6-thioinosine triphosphate; 6-MeTITP: 6-methylthioinosine triphosphate; ITPA: inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase; IMPDH: inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; 6-TXMP: 6-thioxanthosine 5’-monophosphate; GMPS: guanosine monophosphate synthetase; 6-TGMP: 6-thioguanine monophosphate; 6-TGDP: 6-thioguanine diphosphate; 6-TGTP: 6-thioguanine triphosphate; NUDT15: nudix hydrolase 15; 6-TGNs: 6-thioguanine nucleotides; 6-MeTGMP: 6-methythioguanine monophosphate.