Fig. 1 |. Design and evaluation of LNP library for perinatal brain mRNA delivery.
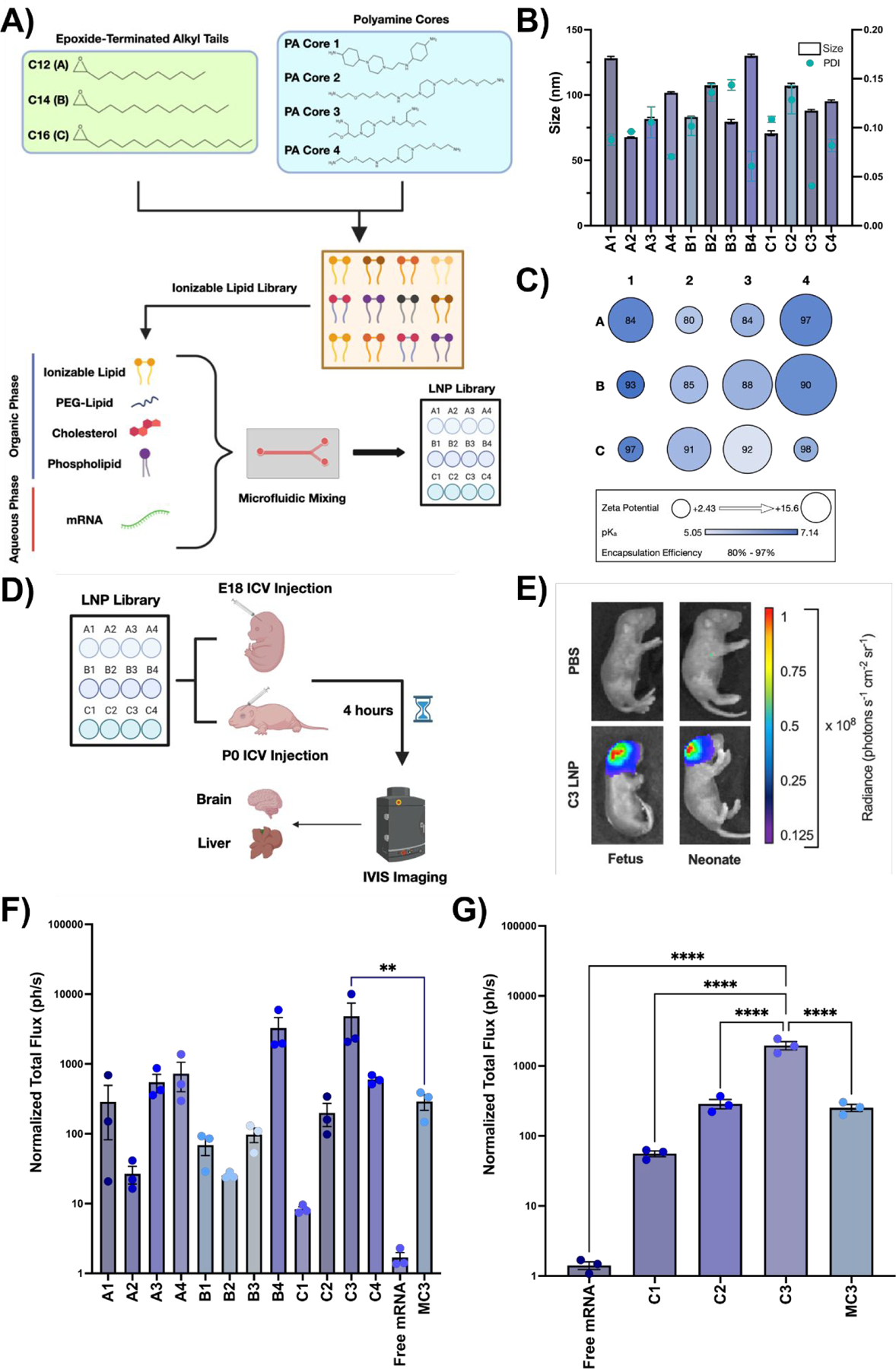
(A) Chemical structures of epoxide-terminated alkyl tails (green box) and polyamine cores (blue box) combined to generate an ionizable lipid library. Formulation of LNPs via microfluidic mixing with an ethanol phase containing ionizable lipid, PEG-lipid, cholesterol, and DOPE and an aqueous phase containing luciferase mRNA is also visualized. LNPs were named based on the alkyl tail length (A-C) and polyamine core (1–4) of the ionizable lipid incorporated into the formulation. (B) Size and PDI of each LNP formulation in the LNP library. (C) Zeta potential (radius of circle), pKa (gradient color), and encapsulation efficiency (centered number) for each LNP formulation. (D) Scheme demonstrating LNP screening in E18 BALB/c fetuses or P0 BALB/c neonates via ICV injection. (E) IVIS imaging showing luciferase expression in a representative C3 LNP-treated fetus (left) and neonate (right) relative to PBS-treated controls. (F) Quantification of luciferase signal from fetal brains treated with each LNP. (G) Quantification of luciferase signal from the neonatal brains treated with a subset of LNPs. All luminescence readings are represented as normalized total flux. ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post-hoc Dunnett’s test compared to MC3 (fetus) and C3 (neonate). Outliers were detected using Grubbs’ test and removed from analysis; minimum n = 3 per treatment group; error bars represent SEM.
