Figure 2. Variants in various classes of genomic elements have diverse effects on gene expression and protein translation.
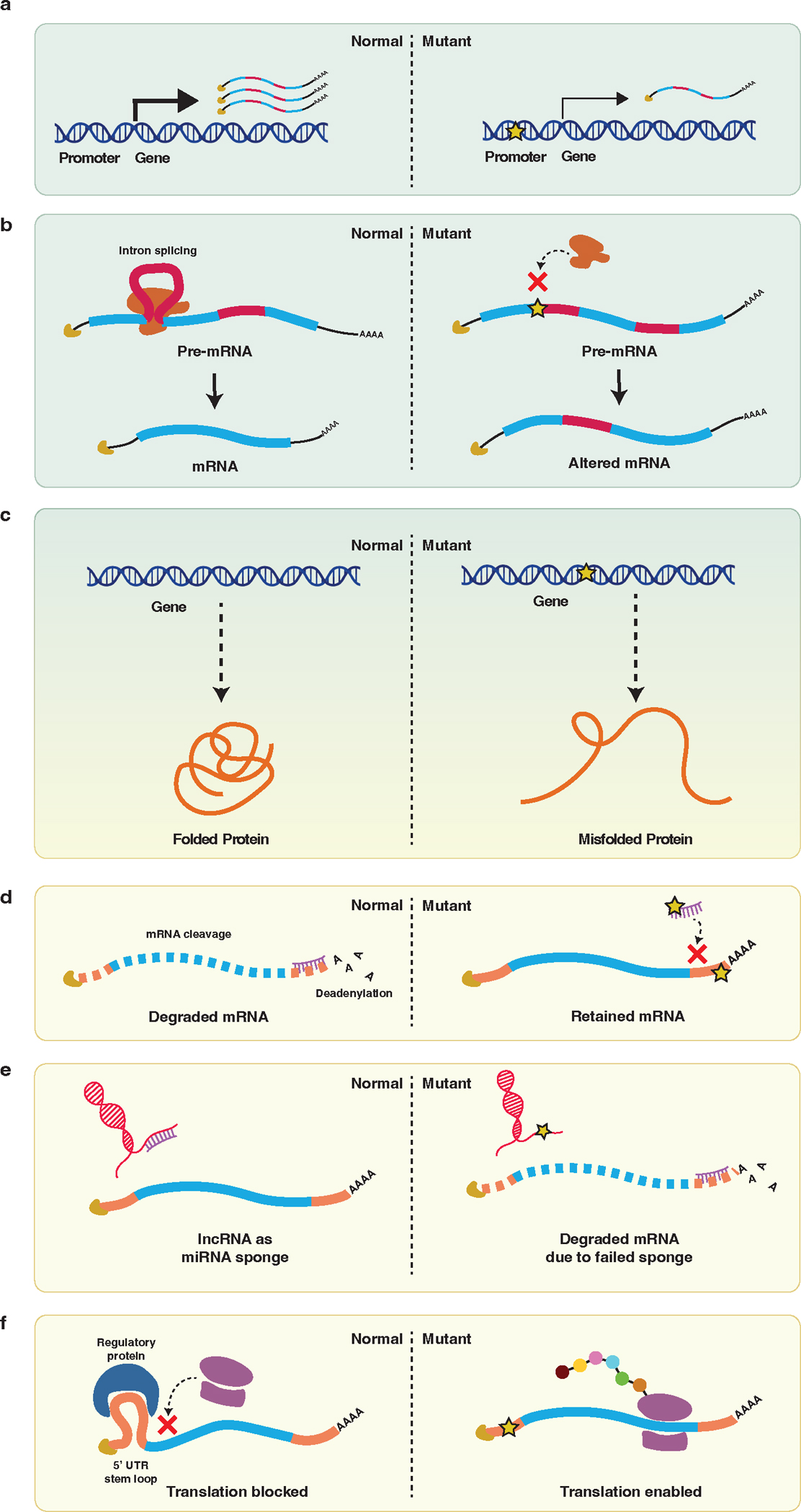
(a) Promoter and enhancer variants, as well as some types of lncRNA variants, disrupt the regulation of gene expression, decreasing transcription. (b) Splice site variants can result in abnormally spliced transcripts and the production of altered protein. (c) Coding variants can disrupt protein function by various mechanisms, including protein misfolding. (d) Variants in miRNA or 3’ UTR sequences can disrupt miRNA-mediated regulation of mRNA transcript abundance, resulting in mRNA retention. (e) Variants in some types of lncRNAs can disrupt the ability of lncRNAs to function as an miRNA sponge, resulting in mRNA degradation. (f) 5’ UTR variants can alter binding of regulatory proteins, resulting in altered translation.
