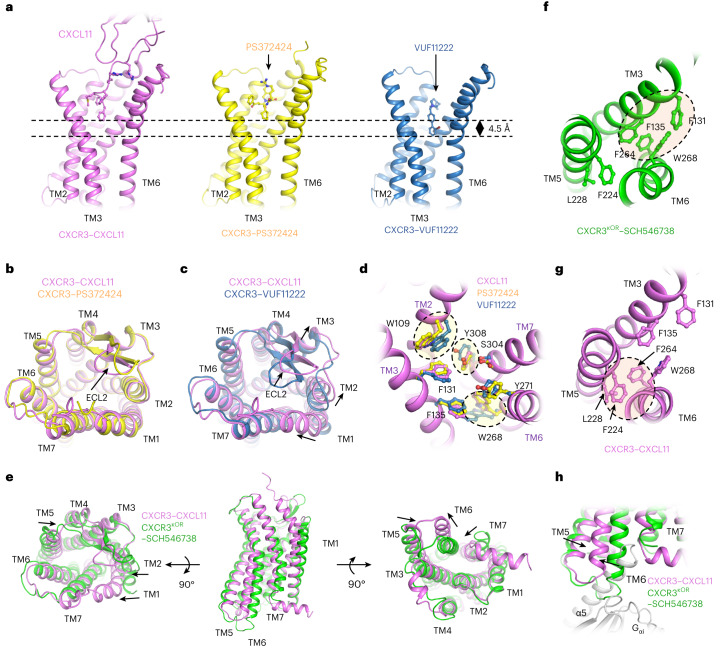
Fig. 5. Activation of CXCR3 by agonists of different types.
a, Comparison of the insertion depth of the three agonists. The receptors are shown as cartoons and the ligands are shown as sticks. CXCL11, PS372424 and VUF11222 are colored violet, yellow and blue, respectively. b, Superposition of CXCL11-activated CXCR3 (violet) and PS372424-activated CXCR3 (yellow). c, Superposition of CXCL11-activated CXCR3 (violet) and VUF11222-activated CXCR3 (blue). d, The residues in CXCR3 involved in the interactions with CXCL11 (violet), PS372424 (yellow) and VUF11222 (blue). The residues are shown as sticks, and the CXCL11-activated CXCR3 are shown as cartoons. e, Comparison of CXCL11-activated CXCR3 (violet) and SCH546378-inhibited CXCR3 (green). f, The packing between TM3 and TM6 in the CXCR3 inhibited by antagonist SCH546738. CXCR3 is shown as a cartoon model and colored green and residues involved in TM packing are shown as sticks. g, The packing between TM5 and TM6 in the CXCR3 activated by chemokine CXCL11. CXCR3 is shown as a cartoon model and colored violet, and residues involved in TM packing are shown as sticks. h, Outward displacement of TM6 on CXCL11 binding leads to the exposure of the Gαi binding pocket. The CXCL11-activated CXCR3, SCH546378-inhibited CXCR3 and Gαi are shown as cartoon and colored violet, green and gray, respectively.