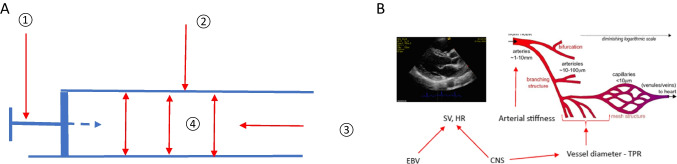
Fig. 1.
A Schematic presentation of fluid flow in the pipe: (1) pushing force; (2) pipe stiffness; (3) fluid viscosity and volume; (4) the pressure exerted by the fluid on the walls of the pipe. Unlike the arterial system, the resistance to flow in a pipe is the viscosity and volume of the fluid (3). B Schematic presentation of circulatory system and main determinants of blood pressure. The pulse wave causes an increase in SBP from the aorta, through the elastic arteries, to the muscular arteries. Despite the higher SBP in these segments of the arterial system, the mean arterial pressure is lower in them than in the aorta, which ensures the maintenance of blood flow. In the resistance arteries (arterioles), there is a large decrease in arterial pressure and a gradual decrease in the difference between SBP and DBP.
Adapted from Keelan J, Hague JP (2021) Sci Rep 11:5408. CNS, central nervous system; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; EBV, effective blood volume; HR, heart rate; SBP, systolic blood pressure; SV, stroke volume; TPR, total peripheral resistance