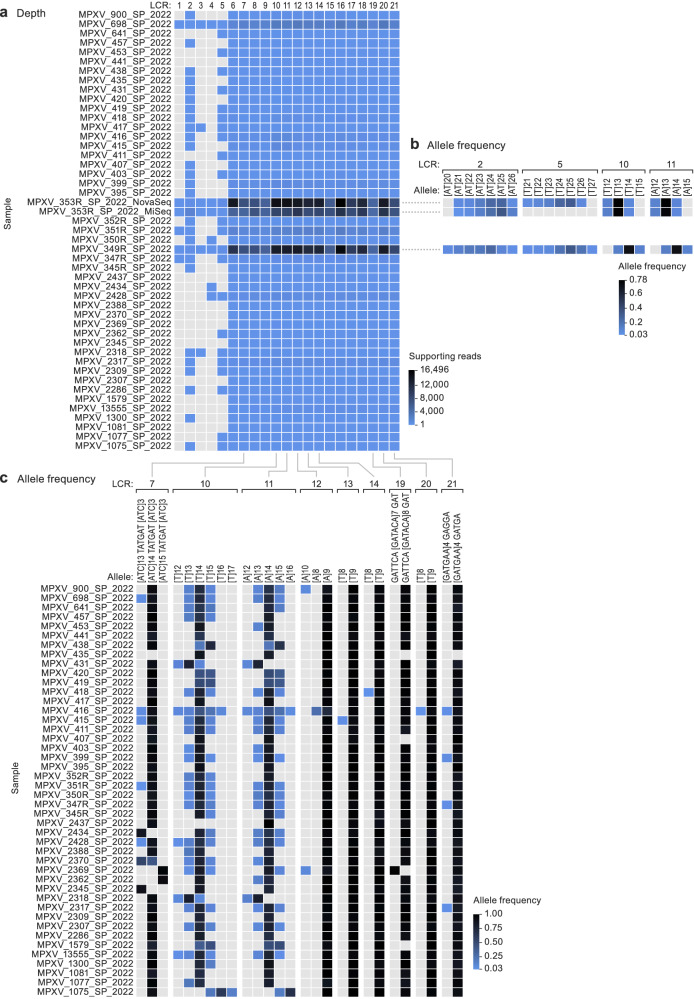
Fig. 4. Low-complexity regions (LCRs) might be more phylogenetically informative than single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for inter-host sequence analysis.
Monkeypox virus (MPXV) population genomics within the biological specimen (intra-host) and across different specimens (inter-host). a Panel shading indicates the number of reads supporting each LCR for each sample. Only paired reads that include a perfect match to both flanking regions were counted; the gradient shows the maximum value in black and the minimum value (n = 1) in the lightest blue. Samples without coverage are indicated in gray. b Comparison of LCR allele frequency for samples 353R and 349R. Only LCRs with at least 10 supporting paired reads including both flanking regions were counted; only alleles with a frequency of 0.03 or higher were considered. The gradient shows the maximum value in black and the minimum value (n = 0.03) in the lightest blue. c Comparison of LCR allele frequency in all samples for LCRs with good coverage (7, pair 10/11, 12, 13, 14, 19, 20, and 21). Only LCRs with at least 10 supporting paired reads including both flanking regions were counted; only alleles with a frequency of 0.03 or higher were considered. The gradient shows the maximum value in black and the minimum value (n = 0.03) in the lightest blue.