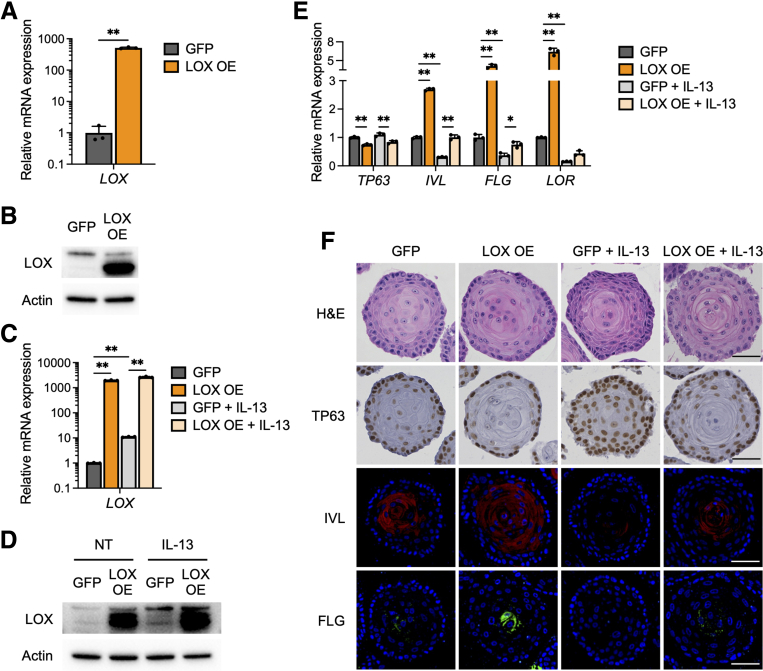
Figure 2.
LOX overexpression promotes cell differentiation in esophageal epithelium. (A) qRT-PCR for LOX of monolayer-cultured EPC2-hTERT cells overexpressing GFP or LOX OE (n = 3). (B) Representative immunoblot for LOX of the monolayer-cultured GFP and LOX OE cells. (C–E) IL13 treatment induces aberrant LOX expression in EPC2-hTERT organoids. GFP and LOX OE organoids were cultured with or without IL13 (10 μg/mL) from days 7 to 11 and then harvested on day 11. (C) qRT-PCR and (D) immunoblot for LOX in GFP and LOX OE cells, monolayer-cultured with or without IL13. (E) qRT-PCR for SOX2, KRT14, TP63, IVL, FLG, and LOR of the GFP and LOX OE organoids (n = 3). (F) Representative images of H&E staining, immunohistochemistry for TP63, and immunofluorescence staining for IVL (red), FLG (green), and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue), in the GFP and LOX OE organoids. Scale bar: 50 μm. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments and expressed as means ± SDs. (A) A 2-tailed Student t test and (C and E) 1-way analysis of variance were performed for statistical analyses. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01.