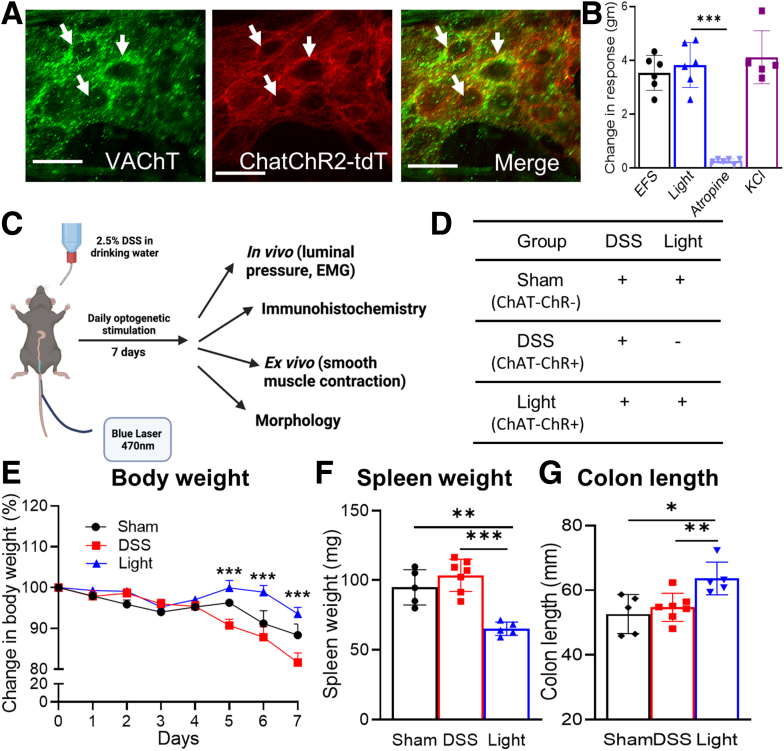
Figure 3.
Optogenetic activation of enteric cholinergic signaling reduces inflammatory indices in DSS-induced colitis. (A) ChAT-ChR2 mice co-express tdT and VAChT, confirming cholinergic-specific expression of ChR2 in myenteric neurons (white arrows). (B) BLS leads to smooth muscle contractility in colons isolated from ChAT-ChR2 mice, similar to the response seen with EFS and KCl, and this response is abrogated by pretreatment with atropine (n = 6). (C) Mice were treated with DSS for 7 days, during which they received daily intraluminal BLS to activate colonic cholinergic neurons. (D) Control groups included sham and DSS groups, as shown. Weight loss was reduced markedly in the (E) Light group (sham, n = 5; DSS, n = 7; light, n = 5), as was (F) splenomegaly (sham, n = 5; DSS, n = 7; light, n = 5). (G) Colonic shortening (sham, n = 5; DSS, n = 7; light, n = 5) also was preserved. Scale bars: 50 μm. Data are shown as means ± SEM. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001.