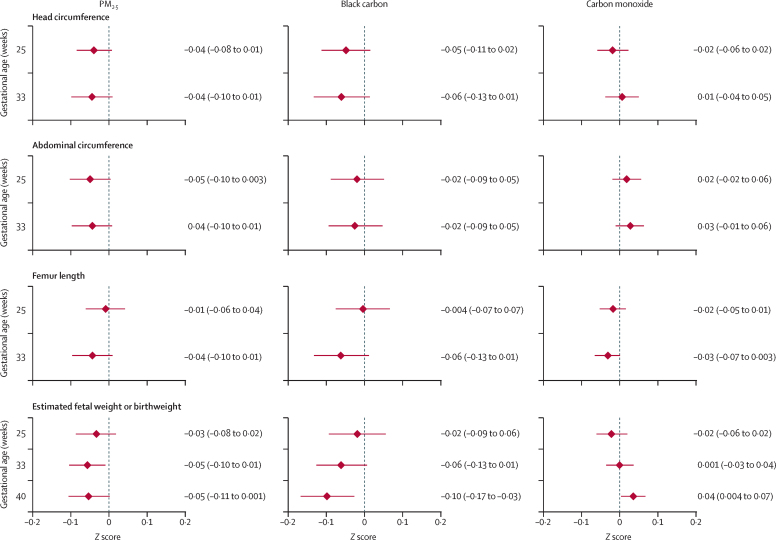
Figure 4.
Results of exposure–response analyses of head circumference, abdominal circumference, femur length, and estimated fetal weight or birthweight Z scores scaled to the interquartile difference of PM2·5, black carbon, and carbon monoxide and estimated at 25, 33, and 40 weeks (for the estimated fetal weight Z score only)
Differences were estimated from generalised additive mixed models (by pollutant) of the fetal growth Z scores as a function of a smooth surface comprising gestational age and pollutant concentrations and adjusted for potentially confounding variables (socioeconomic status, maternal age, nulliparity, diet diversity, maternal education, maternal haemoglobin, and second-hand smoke). Each of the 12 panels corresponds to the combination of fetal growth Z score and personal exposures to each pollutant. Values lower than 0 indicate a lower Z score for the interquartile difference of each pollutant (ie, household air pollution worsens fetal growth Z scores), whereas values higher than 0 indicate higher Z score for the interquartile difference of each pollutant. The estimated mean differences are displayed with a diamond and corresponding 98·75% CIs as horizontal lines. PM2·5=fine particulate matter.