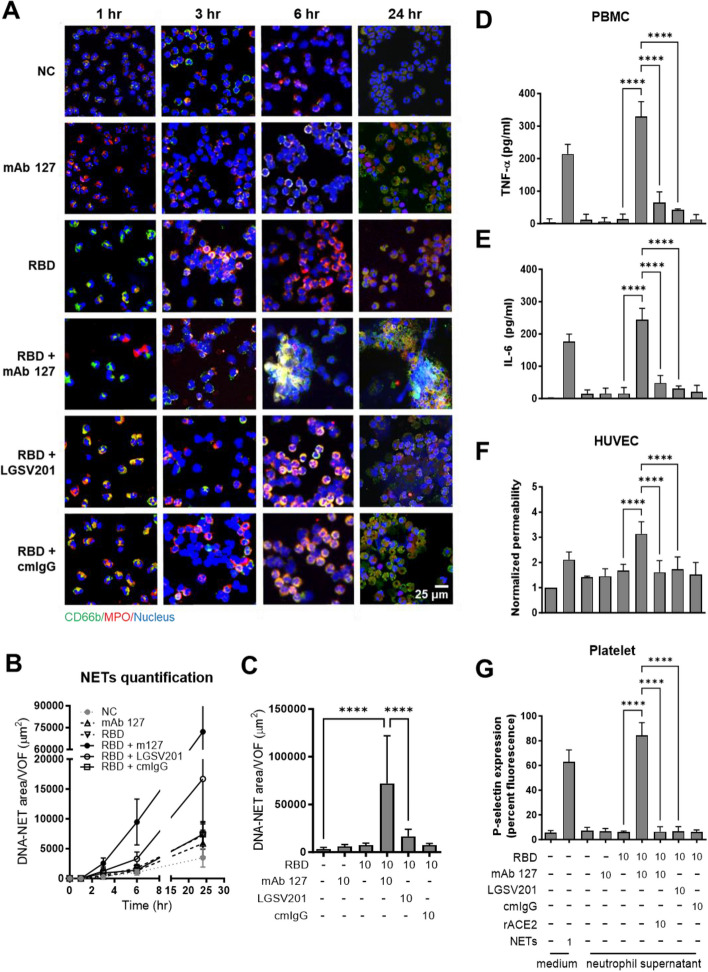
Fig. 3.
NETosis triggered by CR Abs in the presence of RBD drives thrombosis-associated cell activation. (A) Isolated human neutrophils were treated with 10 μg/mL recombinant RBD protein and the indicated antibodies (mAbs 127, LGSV201, or cmIgG, 10 μg/mL) or not. After the indicated time points, the cell suspensions were spun onto a microscope slide by using a cytocentrifuge, fixed and stained with anti-CD66b antibody (green), anti-MPO antibody (red) and DAPI (blue) nuclear stain and then visualized using immunofluorescence staining. The area of NET formation at (B) different time points or (C) 24 h after stimulation was quantified by ImageJ. Views for NET quantification were randomly selected with 9 pictures from each experiment. The supernatants of neutrophils were harvested after different treatments and further administered to isolated human PBMCs, HUVECs, or platelets. Purified PMA-induced NETs (1 μg/mL) were used as the positive control, and in some experiments, rACE2 was added. Following 24 h of stimulation with neutrophil-conditioned media, PBMC supernatants were collected to measure the (D) TNF-α and (E) IL-6 levels using ELISA kits. (F) Endothelial barrier integrity was determined by a Transwell permeability assay, as described in the Materials and Methods. (G) After 15 min of stimulation, the percent fluorescence of P-selectin surface expression on platelets was measured by anti-CD62p FITC-conjugated antibodies and further analyzed by cytoFLEX. The averages of triplicate cultures ± SD are shown. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test, ****p < 0.0001. Bar: 25 μm