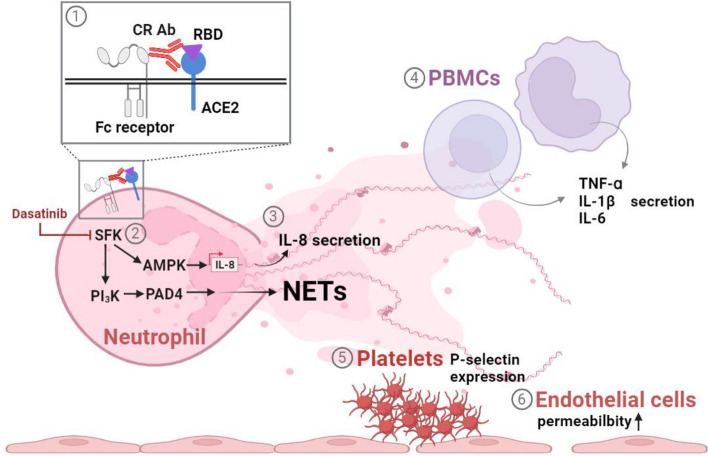
Fig. 8.
The potential mechanisms underlying CR Ab-induced thrombosis. (1) CR Abs binding to RBD and ACE2 as well as Fc receptors on the surface of neutrophils induce signaling pathways. (2) Signaling pathways that regulate IL-8 secretion and NET formation are activated: SFK-AMPK signaling mediates IL-8 secretion, while SFK-PI3K-PAD4 signaling mediates NET formation. The actions of both IL-8 and NETs could be suppressed by dasatinib, which is an SFK inhibitor. (3) Secreted IL-8 and NETs subsequently cause (4) the secretion of TNFα, IL-6, and IL-1β from PBMCs, (5) enhanced expression of surface P-selectin on platelets, and (6) increased endothelial permeability. These processes collectively contribute to the eventual formation of thrombi. CR Ab, ACE2-cross-reactive RBD antibodies; ACE2, angiotensin converting enzyme-2; RBD, SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain; IL-8, interleukin-8; NETs, neutrophil extracellular traps; SFK, Src family kinases; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PAD4, protein arginine deiminase 4; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Created with BioRender.com