Fig. 4.
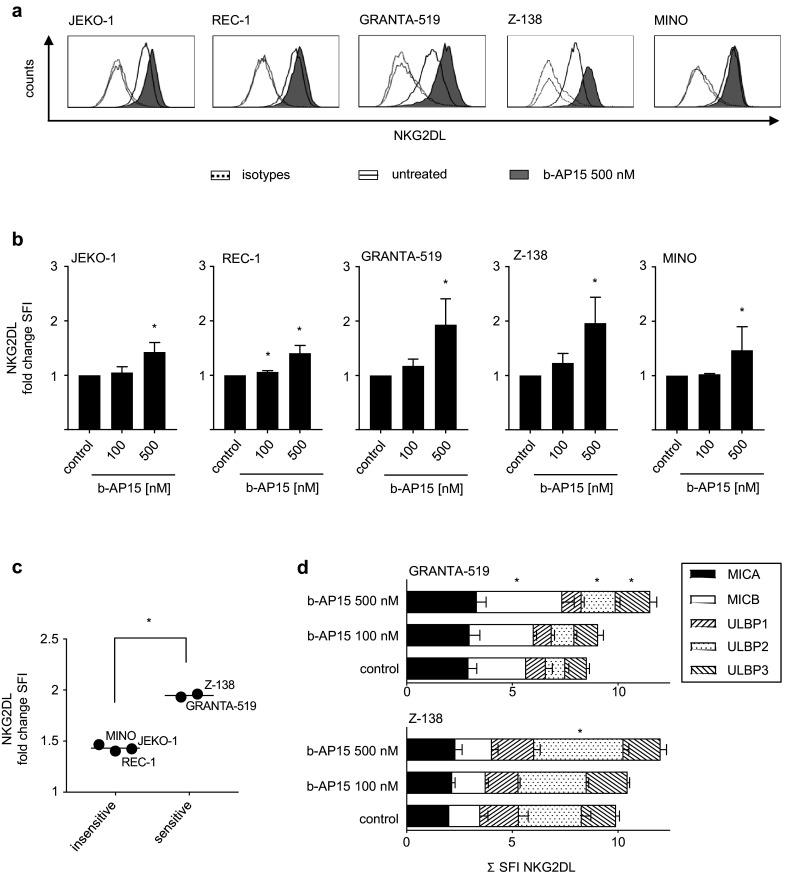
b-AP15 differentially induces NKG2DL expression in MCL cells. MCL cells were exposed to the indicated concentrations of b-AP15 or were left untreated for 24 h. Expression of NKG2DL was determined by flow cytometry using either pooled (a–c) or individual (d) monoclonal antibodies against MICA, MICB and ULBP1-3 or isotype control followed by PE-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibody. a Exemplary results of stainings with pooled NKG2DL antibodies are shown for the indicated MCL cell lines. b SFI levels obtained by staining with pooled antibodies are shown for the indicated cell lines; changes of NKG2DL surface expression are represented as fold change in SFI of b-AP15-treated cells over untreated cells. Combined results of at least two independent experiments are shown. Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance between control and treated cells (*p < 0.05). c Mean fold change in SFI of NKG2DL expression of b-AP15-treated cells over untreated cells is shown for sensitive (GRANTA-519, Z-138) and insensitive (REC-1, MINO, JEKO-1) MCL cell lines. Bars represent mean. Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance of differences between sensitive and insensitive cell lines (*p < 0.05). d Exemplary results of stainings with individual NKG2DL antibodies are shown for the indicated MCL cell lines. Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance between control and treated cells (*p < 0.05)
